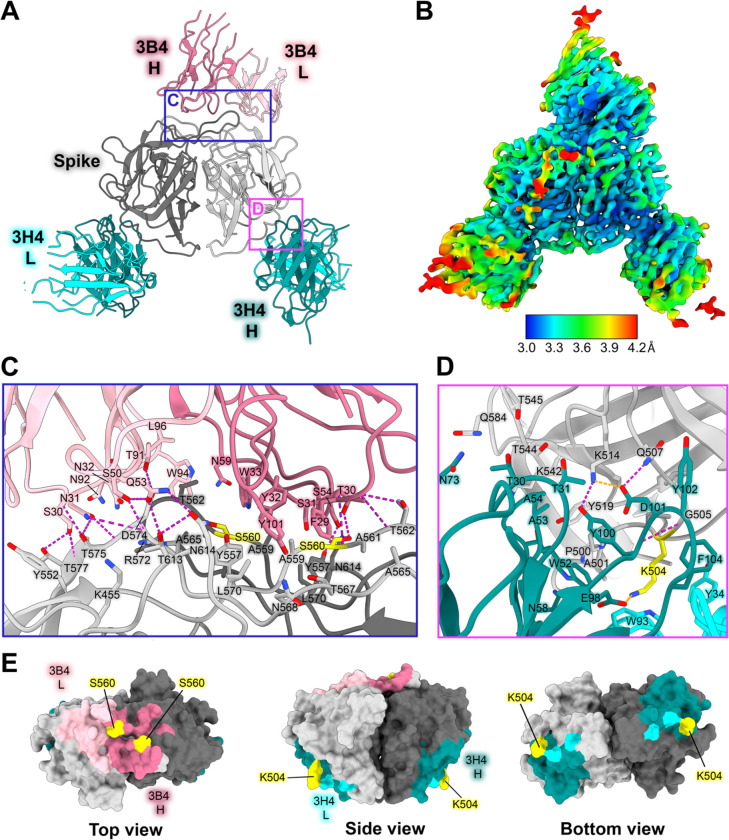
Figure 4: Neutralizing antibody 3H4 binds to a unique epitope at the base of the spike, and neutralizing antibody 3B4 has a unique top epitope in which a single antibody binds the spike dimer interface.
(A) Single-particle cryoEM reconstructed map solved to FSC0.143 3.33 Å of neutralizing Fab 3H4 and Fab 3B4 bound simultaneously to the HAstV1 spike, displayed as a ribbon model with 3H4 colored cyan and 3B4 colored pink. The heavy and light chains are colored in dark and light shades, respectively. Red panels show the locations of the focused views shown in panel C and D. (B) Local resolution estimation of the cryoEM structure of HAstV1 spike bound to 3H4 Fab and 3B4 Fab, with contour level at 0.043 in ChimeraX. (C) Focused view of the 3B4 epitope, with the light chain colored light pink, and the heavy chain colored dark pink, with hydrogen bond interactions colored magenta. Serine 560, which was previously identified as a residue that overcomes the neutralization activity of 3B4 when mutated to proline, is highlighted in yellow. (D) Focused view of the 3H4 epitope, with the light chain colored light cyan, and the heavy chain colored dark teal. Hydrogen bond interactions are colored magenta and salt bridges are colored in orange. Lysine 504, which was previously identified as a residue that overcomes the neutralization activity of 3H4 when mutated to glutamic acid, is highlighted in yellow. (E) Surface view of the HAstV1 spike with antibody interacting residues colored according to antibody chain. Residues interacting with both chains are colored according to the predominant interaction. Residues that confer resistance to the respective antibody when mutated are colored in yellow.