Fig. 1.
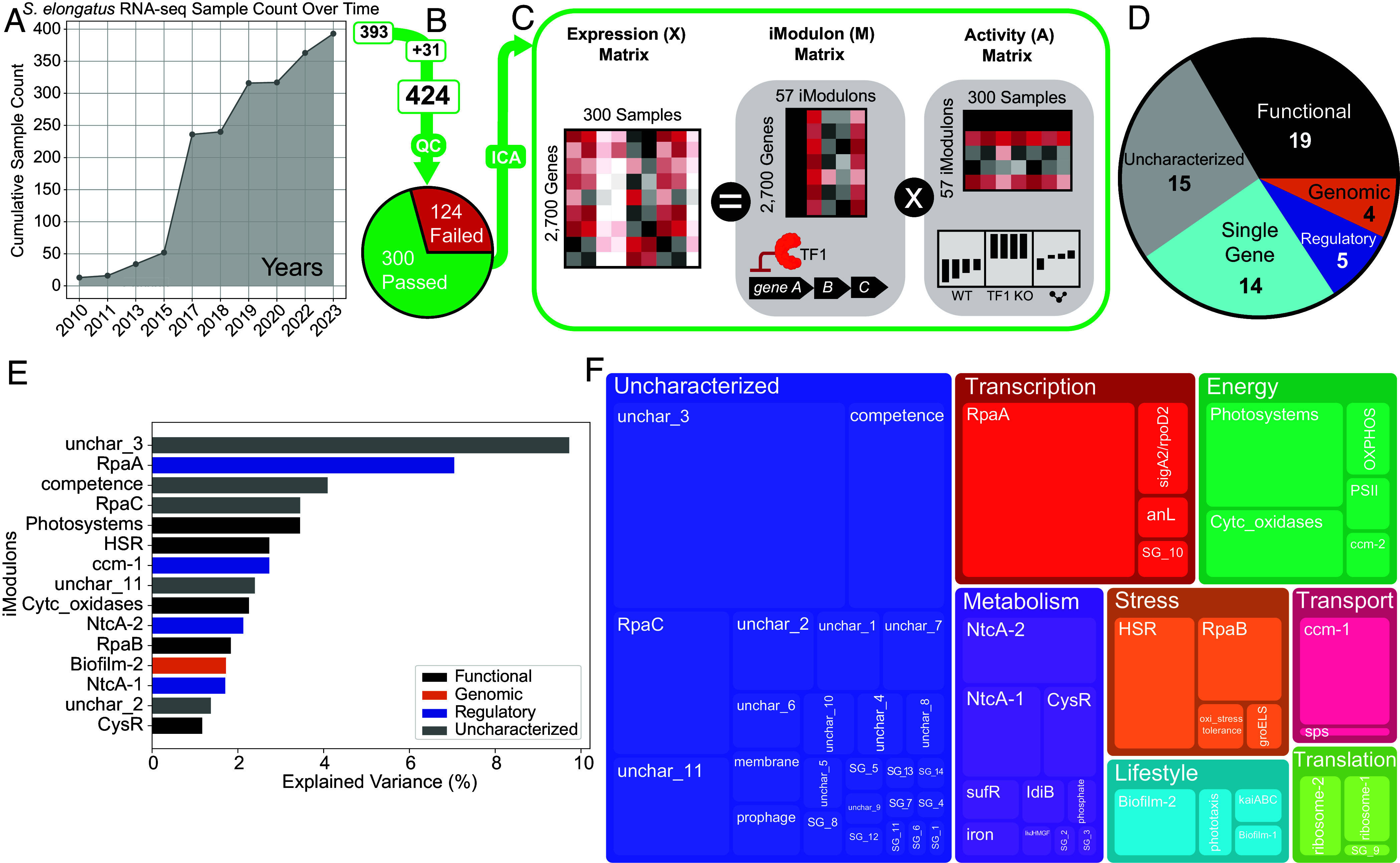
ICA decomposes the transcriptome of S. elongatus PCC 7942. (A) Line graph depicting the increase in publicly available high-throughput RNA-seq for S. elongatus as seen in NCBI’s SRA database over time. (B) The 393 public samples were combined with 31 new in-house samples and processed using our RNA-seq and quality control pipeline. The final dataset contains 300 high-quality samples. (C) ICA takes in the expression data matrix X (2,700 genes × 300 samples) and produces the iModulon matrix M (2,700 genes × 57 iModulons) and Activity matrix A (57 iModulons × 300 samples). The condition-independent iModulon matrix demonstrates the relationship between iModulon genes and an underlying biological signal, while the condition-dependent activity matrix corresponds to the activity level of the iModulon across different experimental conditions in the compendium. (D) Main categories of the 57 iModulons. Regulatory iModulons have significant overlaps with a known regulon, while Genomic iModulons result from genomic changes such as knockouts. Functional iModulons are iModulons that are related to a particular biological function but are not linked to a specific regulator. Single Gene iModulons contain one gene that has a significantly higher weighting than all other genes, and Uncharacterized iModulons contain genes whose functions are yet to be defined. (E) Top 15 iModulons with the highest explained variance and their categories. (F) Treemap showing biological and functional categories of all 57 iModulons. The sizes of the boxes represent the explained variance of the corresponding iModulon. The explained variance of each iModulon is knowledge-based and biologically meaningful, as the iModulons are annotated with specific functional roles.
