Figure 1.
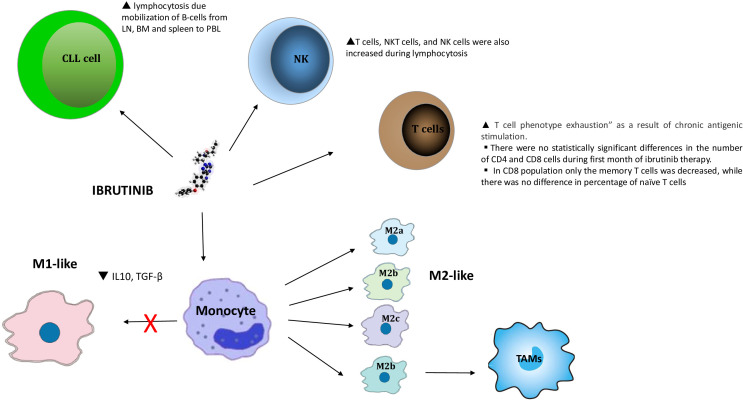
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells depend on interactions with the microenvironment. BTK inhibitors produce transient lymphocytosis caused by the mobilization of B-cells from LN, bone marrow and spleen to peripheral blood. They also produce changes in the tumor environment due to a decrease in the expression of immunosuppressive molecules such as PD-L1, IL-10, CD200 or BTLA in CLL B-cells. The heterogeneity and characterizations of macrophages. Macrophages could be roughly divided into two subtypes (M1-like and M2-like, while M2-like macrophages can be further differentiated into M2a, M2b, M2c, and M2d phenotypes.) depending on their different microenvironmental stimuli. All of these phenotypes express different cytokines, chemokines, and receptors which give rise to their different functions respectively. Generally, M1-like macrophages mainly induce proinflammatory responses and usually associated with Th1 response while M2-like macrophages contribute trophism and tissue tolerance. Furthermore, M2a is mainly mediating tissue repair and remodeling and Th2 responses; M2b is commonly responsible for immunoregulation; M2c mainly functions in phagocytosis, and M2d participates in angiogenesis in tumor. MC2 TYPE MACROPHAGE: M2c is stimulated by Il-10 and discharges CCL 16 and CCL 18 chemokines. The concentration of this cytokine was statistically significant lower at day 14 and at day 30 in comparison to pre-treatment concentration (day 0).