Abstract
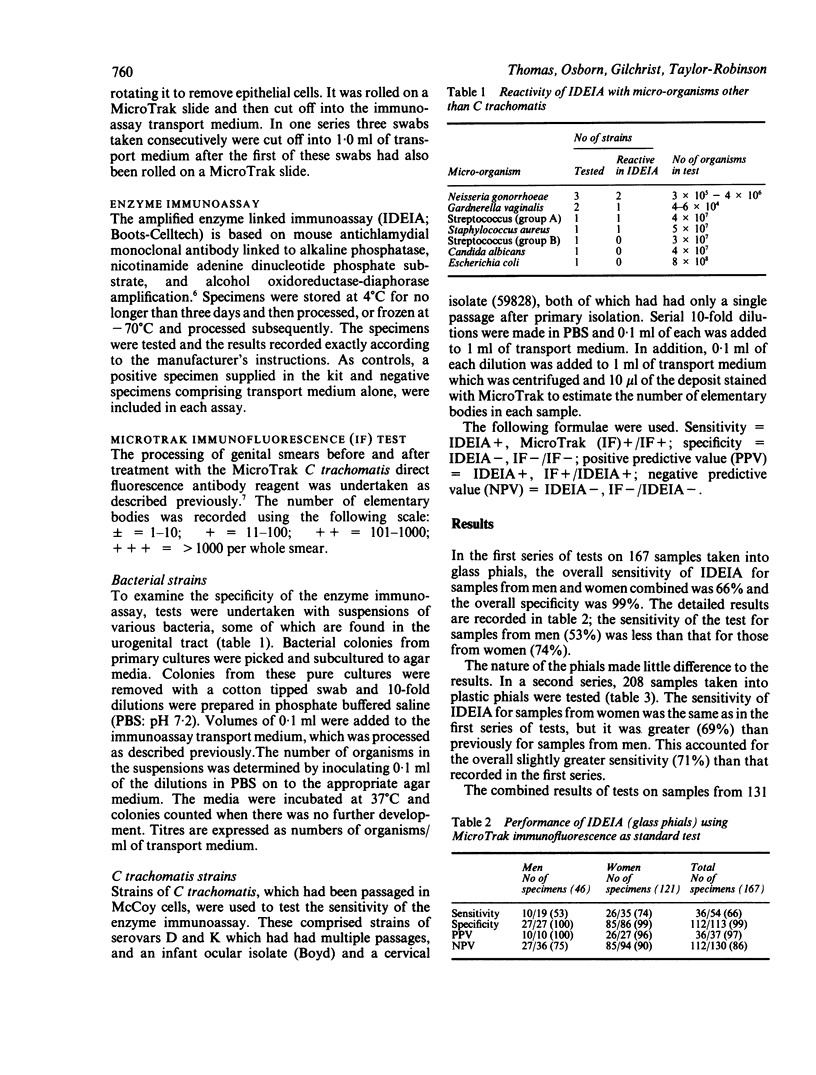
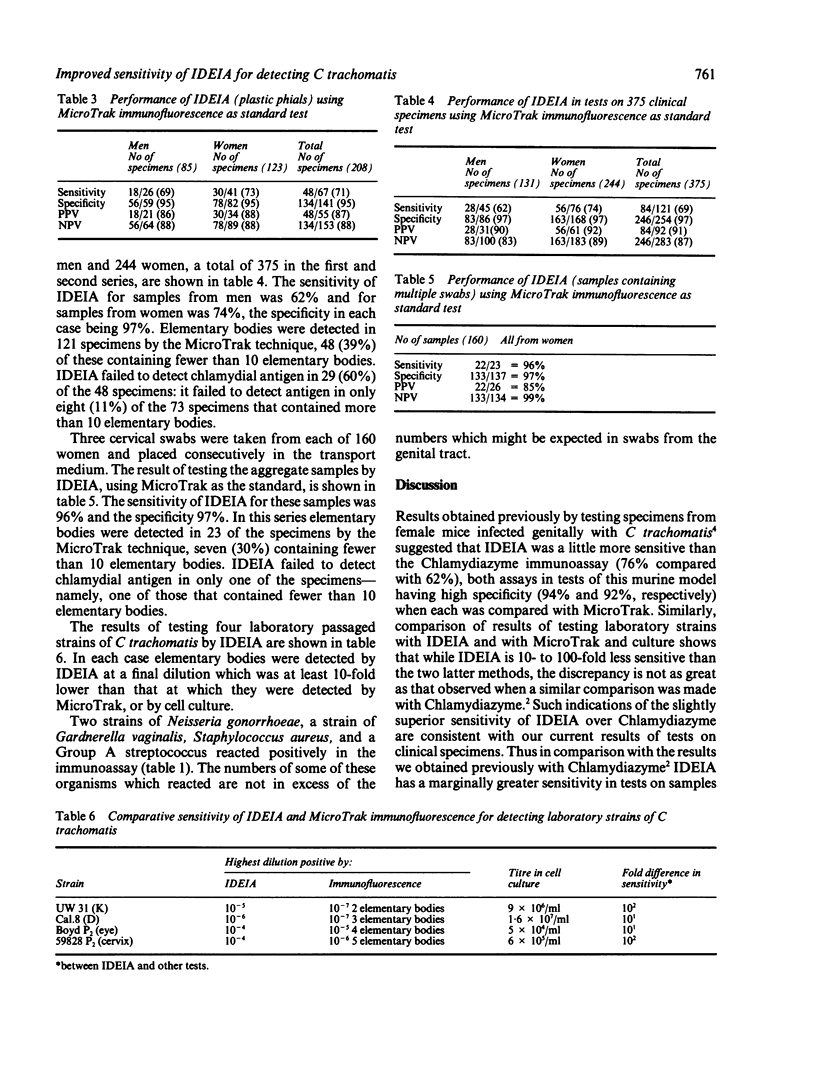
In tests on 375 genital tract specimens a commercially available enzyme immunoassay for Chlamydia trachomatis (IDEIA; Boots-Celltech) was found to have sensitivity values of 62% for men and 74% for women, and a specificity of 97% for both groups, relative to the results obtained by a fluorescence assay (Micro Trak; Syva). The positive predictive value and the negative predictive value of the immunoassay were 91% and 87%, respectively. Collection of samples for IDEIA in transport medium in plastic phials, as opposed to glass phials recommended by the manufacturer, had no effect on these values. Tests of the sensitivity of IDEIA using laboratory strains of C trachomatis showed that the assay detected chlamydial elementary bodies only at dilutions at least 10-fold lower than those at which they could be detected by Micro Trak. Tests of the specificity of the assay with microorganisms found in the genital tract, other than chlamydiae, showed that reactions occurred with a number of these. Testing three cervical swabs from the same patient, with the material taken into a single phial of transport medium, increased the sensitivity of IDEIA from 74% to 96%, without reducing the specificity which remained at 97%. It is concluded that this approach enchances the value of the test in a sexually transmitted disease clinic population and may do so in a population with a low prevalence of chlamydiae.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Grillner L., Beckman S., Hammar H. Comparison of two enzyme immunoassays and an immunofluorescence test for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;5(5):559–562. doi: 10.1007/BF02017705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard L. V., Coleman P. F., England B. J., Herrmann J. E. Evaluation of chlamydiazyme for the detection of genital infections caused by Chlamydia trachomatis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):329–332. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.329-332.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilleyman J. S. Gerard Slavin: editor, Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978-1988. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Jan;41(1):1–2. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilleyman J. S. Gerard Slavin: editor, Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978-1988. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Jan;41(1):1–2. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty K. C., O'Neill J. J., Hambling M. H. Comparison of enzyme immunoassays and cell culture for detecting Chlamydia trachomatis. Genitourin Med. 1986 Jun;62(3):175–176. doi: 10.1136/sti.62.3.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh S. F., Slack R. C., Caul E. O., Paul I. D., Appleton P. N., Gatley S. Enzyme amplified immunoassay: a novel technique applied to direct detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in clinical specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Oct;38(10):1139–1141. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.10.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Thomas B. J., Osborn M. F. Evaluation of enzyme immunoassay (Chlamydiazyme) for detecting Chlamydia trachomatis in genital tract specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Feb;40(2):194–199. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Tuffrey M. Comparison of detection procedures for Chlamydia trachomatis, including enzyme immunoassays, in a mouse model of genital infection. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Sep;24(2):169–173. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B. J., Evans R. T., Hawkins D. A., Taylor-Robinson D. Sensitivity of detecting Chlamydia trachomatis elementary bodies in smears by use of a fluorescein labelled monoclonal antibody: comparison with conventional chlamydial isolation. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jul;37(7):812–816. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.7.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjiam K. H., van Heijst B. Y., van Zuuren A., Wagenvoort J. H., van Joost T., Stolz E., Michel M. F. Evaluation of an enzyme immunoassay for the diagnosis of chlamydial infections in urogenital specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):752–754. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.752-754.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


