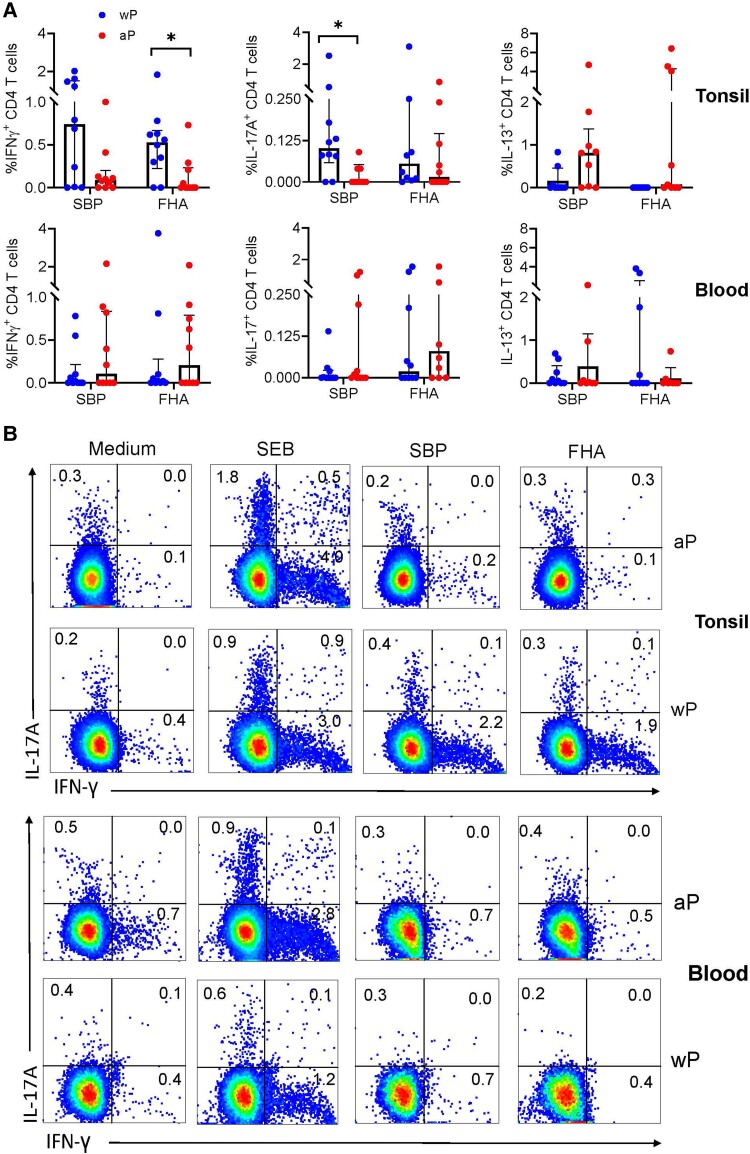
Figure 1.
Significantly higher frequency of IFN-γ and IL-17A–producing CD4 T cells were found in tonsil of adults primed with wP compared with aP vaccines as children. Tonsil and blood samples were isolated from adult donors who had received wP (n = 10) or aP (n = 10) vaccines as children. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells or tonsil mononuclear cells were stimulated with medium (negative control), SEB (positive control), SBP, or FHA, and cytokine-producing CD4 T cells were quantified by surface staining, intracellular cytokine staining, and flow cytometry. A, Frequency of IFN-γ+, IL-17A+, or IL-13+ CD4 T cells that respond to SBP or FHA in blood and tonsil (the frequency of cytokine-positive cells in the medium control was subtracted from the frequency for antigen-stimulated cells). B, Sample flow cytometry plots. Data shown are median and interquartile range. *P < .05, Mann-Whitney test. Abbreviations: aP, acellular pertussis; FHA, filamentous hemagglutinin; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IL, interleukin; SBP, sonicated Bordetella pertussis; SEB, staphylococcal enterotoxin B; wP, whole-cell pertussis.