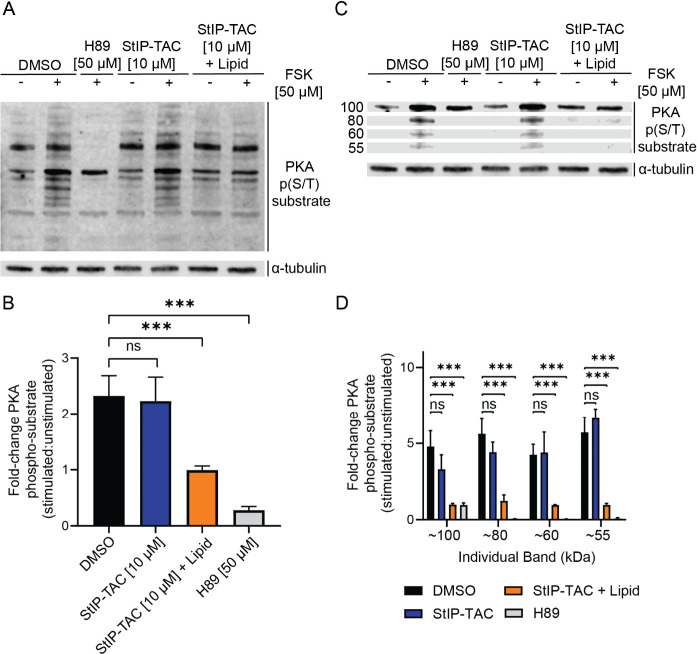
Figure 4.
StIP-TAC treatment inhibits phosphorylation of PKA substrates. (A) Representative Western blot of cells treated with vehicle control, H89, StIP-TAC, or StIP-TAC + SAINT Protein reagent for 5 h with or without 30 min stimulation with 50 μM forskolin (n = 3). Cells treated with H89 and StIP-TAC alongside SAINT protein display a reduction in fold change of total phosphorylated PKA substrate levels after forskolin stimulation. (B) Densitometric quantification of Western blots for three independent experiments (n = 3) demonstrating a statistically significant reduction in total PKA substrate phosphorylation in cells treated with H89 and StIP-TAC with SAINT Protein reagent. Quantification was performed via Li-COR Image Studio. *** p < 0.001; ns, not significant as assessed by one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. Error bars represent standard deviation. (C) Representative Western blot image of select PKA phosphorylated substrates at approximately 55, 60, 80, and 100 kDa bands, demonstrating a prominent reduction in phosphorylation after forskolin stimulation upon treatment with StIP-TAC and SAINT Protein reagent (n = 3). (D) Densitometric quantification of Western blots from three separate experiments (n = 3), demonstrating a statistically significant reduction in phosphorylation of the approximately 55, 60, 80, and 100 kDa substrate bands for cells treated with StIP-TAC and SAINT Protein reagent. Quantification was performed via Li-COR Image Studio. ***p < 0.001; ns, not significant as assessed by one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. Error bars represent standard deviation.