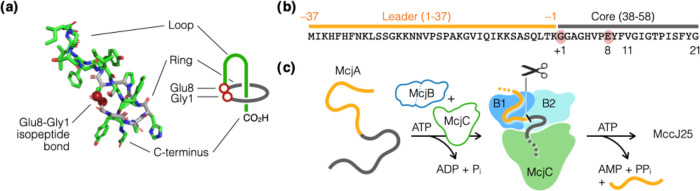
Figure 1.
Unique structure and biosynthetic pathway. (a) MccJ25 contains a macrolactam (the ring) that results from the formation of an isopeptide bond between its Gly1 N-terminal amine and Glu8 side-chain carboxylate. The rest of the peptide folds into a hairpin-like structure (the loop) and passes through the macrolactam to form a “threaded lasso” configuration (PDB: 1PP5).1 (b) The MccJ25 precursor (McjA) is a 58-mer peptide, wherein the leader (orange) and the core (black) peptides are numbered −37 to −1 and +1 to 21, respectively. (c) MccJ25 maturation is carried out by two enzymes: (1) McjB contains two domains, B1 (blue) and B2 (cyan), and are responsible for leader recognition and cleavage, respectively, and (2) McjC (green) catalyzes the formation of the isopeptide bond. Note that McjA, McjB, and McjC are color-coded the same way throughout this manuscript.