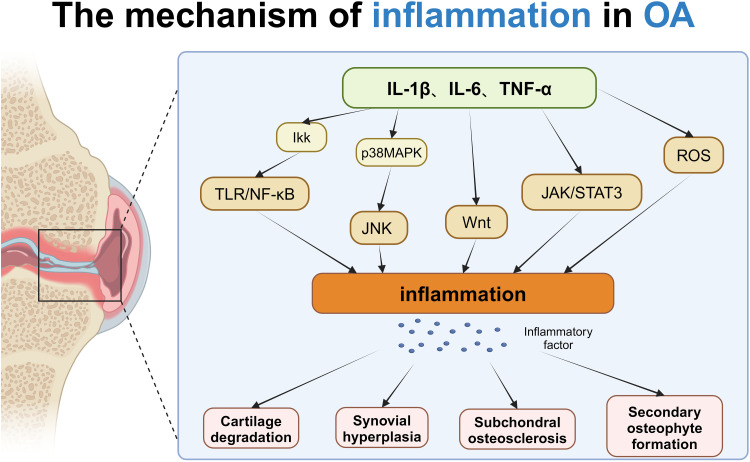
Figure 1.
The mechanism of inflammation in OA: In osteoarthritis (OA), inflammatory factors such as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α trigger inflammation by activating multiple signaling pathways, including the TLR/NF-κB, p38 MAPK, JAK/STAT3, and Wnt pathways. The TLR/NF-κB pathway promotes inflammation through the activation of IKK, while the p38 MAPK pathway exacerbates inflammation via JNK and Wnt signaling, and the JAK/STAT3 pathway is influenced by TNF-α and ROS. These inflammatory signals work together to cause pathological changes such as cartilage degradation, synovial hyperplasia, subchondral osteosclerosis, and osteophyte formation, thus accelerating the progression of OA. Created with BioRender.com.