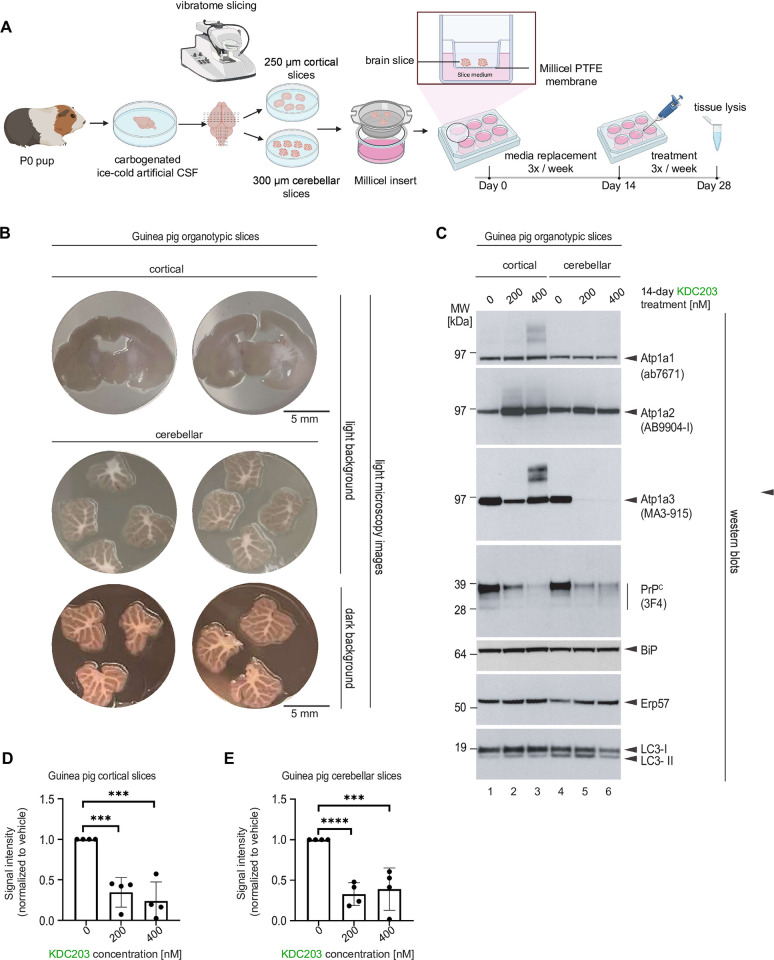
Fig 5. KDC203 lowers PrPC levels in cultured guinea pig cortical and cerebellar brain slices.
(A) Cartoon depicting the workflow for generating cortical and cerebellar guinea pig organotypic brain slices. (B) Microscopy images of cortical and cerebellar guinea pig organotypic brain slices. (C) Western blot analyses of proteins-of-interest following 14-day treatment without or with 200 nM or 400 nM KDC203 in the brain-in-a-dish culture medium. Note that KDC203 exhibited inconsistent effects on the three NKA α subunits, with steady-state Atp1a1 levels being the least affected, Atp1a2 levels elevated in both cortical and cerebellar slices exposed to KDC203, and Atp1a3 levels being differently affected in cortical and cerebellar slices by the presence of KDC203. In contrast, steady-state PrP levels were consistently lower in a KDC203 concentration-dependent manner in both cortical and cerebellar organotypic brain slices. Finally, markers of endoplasmic reticulum stress, BiP and Erp57, or autophagy, LC3, were not significantly altered in the two types of brain slices with or without KDC203 exposure. (D, E) Quantitation of steady-state PrPC levels in vehicle-treated or KDC203-treated cortical (D) or cerebellar (E) brain slices. Significance thresholds indicated in the graphs are based on densitometric analyses of western blot signal intensities from four biological replicates for each treatment group.