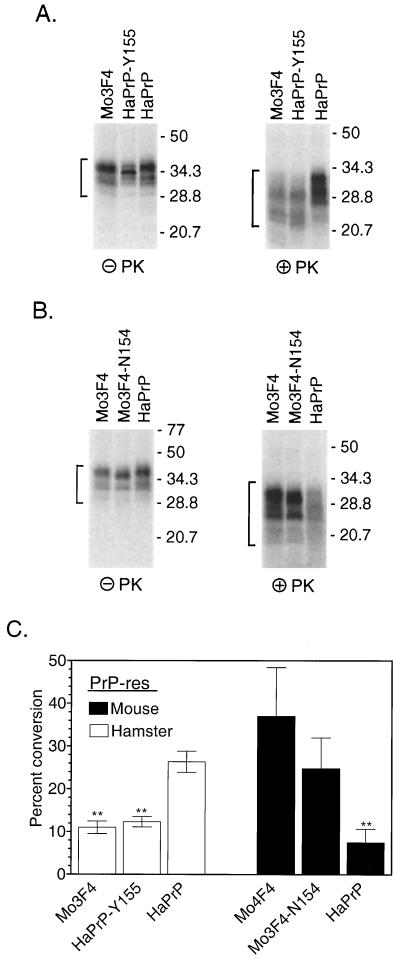
FIG. 4.
Efficient conversion of GPIPOS PrP-sen mutated at amino acid residue 154 or 155 is dependent upon the species of PrP-res. (A and B) Cell-free conversion of mutant (GPIPOS) mouse or hamster PrP-sen by PrP-res derived from scrapie-infected hamster (A) or mouse (B) brains. In each panel, the names of the radiolabeled PrP-sen molecules are indicated above the lanes. HaPrP, hamster PrP. The left panels show 10% of the total reaction mixture without PK treatment but in the presence of the indicated PrP-res constructs and demonstrate that the input amounts of radiolabeled PrP in the reactions were equivalent. The PrP bands which were quantified are indicated by the brackets on the left. The right panels show the remaining 90% of the reaction mixture following digestion with PK. The PrP-res bands which were quantified are indicated by the brackets on the left. The formation of protease-resistant PrP was dependent upon the addition of PrP-res (data not shown). Molecular mass markers in kilodaltons are indicated on the right. Extra lanes were excised from the gels for the purpose of data presentation. (C) Data from four independent repeats of the experiments in panels A and B. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way repeated-measures analysis of variance with Dunnett's post test; double asterisks indicate a P value of <0.001.