Figure 3.
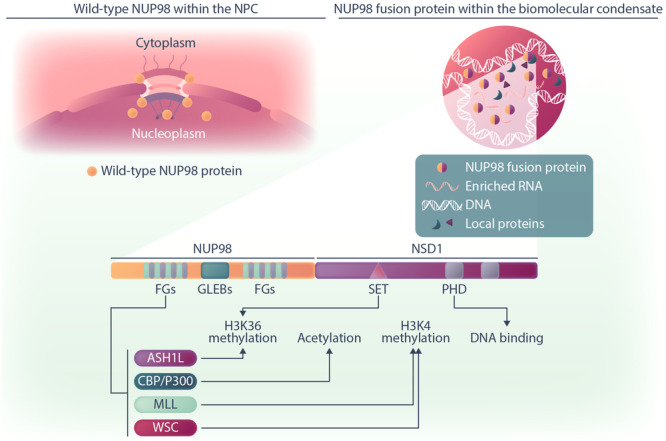
Schematic illustration of the NUP98 protein in healthy cells and interactions of NUP98 fusion proteins in AML cells. The mature wild‐type NUP98 protein is predominantly located in both the nucleus and cytoplasmic regions of the NPC, as well as in the nucleoplasm. The NUP98 fusion proteins are predominantly observed within nuclear punctate structures, known as biomolecular condensates, distributed throughout the nucleoplasm. Within these condensates, NUP98 fusions form their distinct protein interactome, where the N‐terminus FG repeats engage with various regulatory proteins. Specifically, the FG repeats interact with MLL, WSC, CBP/P300, and ASH1L protein complexes, all of which play roles in epigenetic regulation. Simultaneously, functional domains such as PHD and SET in fusion partners like NSD1 collaborate with this regulatory function or engage with chromatin. Figure Made in BioRender.com.
