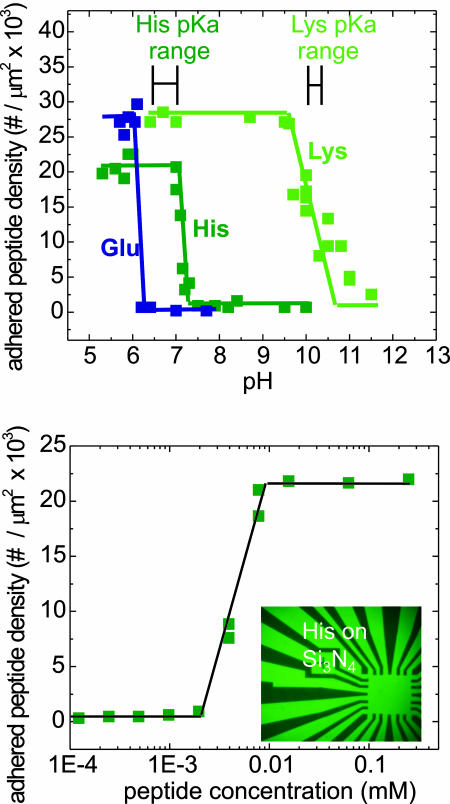
Fig. 4.
Examining mechanisms of amino acid adhesion. (Upper) Titration results examine adhered peptide density as a function of solution pH for three different peptides, each comprised of 10-mers of the respectively labeled amino acids on Si3N4. The predicted pKa of each free amino acid is shown; note the correspondence of adhesion change to each for Lys and His, but not for Glu. (Lower) Adhered peptide density dependence on peptide concentration by using His on Si3N4. Adhesion maintains the saturated value shown here beyond the graph's range up to 1 mM, and the drop to trace amounts occurs at the value roughly calculated to correspond to depletion of the peptide in the solvent, given the solvent volume and substrate area.