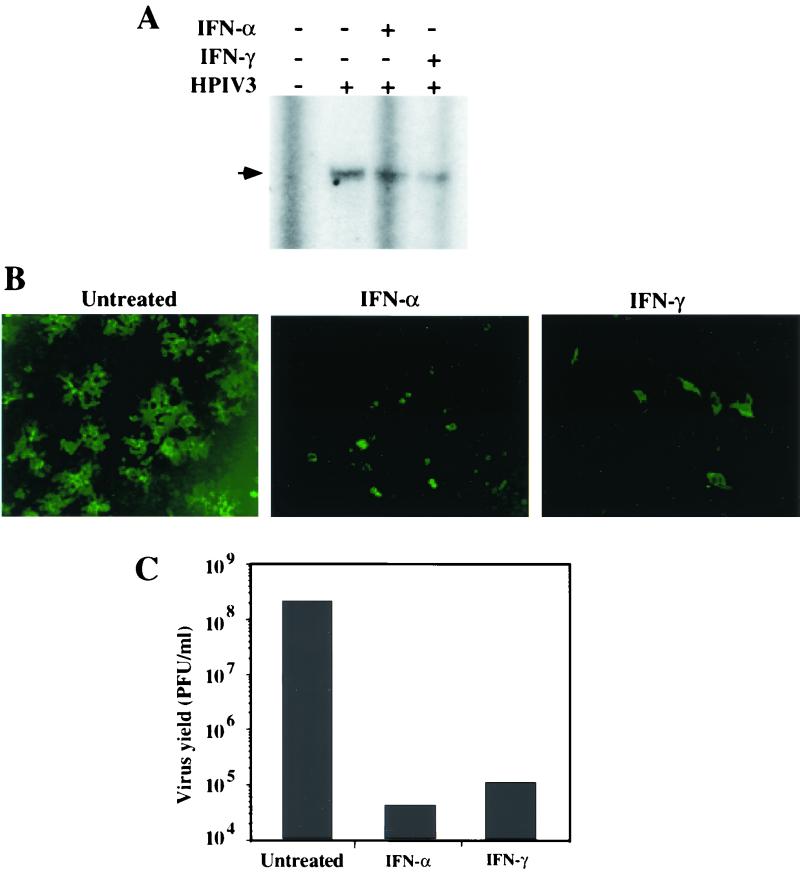
FIG. 5.
Antiviral effects of IFN-α and IFN-γ against HPIV3 in A549 cells. (A) Effects of IFNs on the primary transcription of HPIV3. A549 cells were pretreated with IFN-α or IFN-γ at 1,000 U/ml for 12 h followed by CHX (10 μg/ml) for 2 h. The cells were infected with HPIV3 at a MOI of 5 and incubated in the presence of IFN and CHX. At 6 h postinfection, cells were harvested and accumulation of N mRNA was determined by primer extension analysis as described in Materials and Methods. The arrowhead indicates the 93-nucleotide extension product representing N mRNA synthesis. (B) Effects of IFNs on the accumulation of intracellular viral RNP. The cells, grown on coverslips, were treated with IFNs for 12 h followed by infection with HPIV3 at an MOI of 1.0. At 12 h postinfection, the cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with anti-RNP antibody followed by FITC-conjugated secondary antibody as described in Materials and Methods. (C) Effects of IFNs on the production of infectious HPIV3 virions. The cells were treated with IFNs (1,000 U/ml) for 12 h followed by infection with HPIV3 at an MOI of 0.1. At 40 h postinfection, the release of infectious virions was measured by plaque assay. Results are representative of three independent experiments.