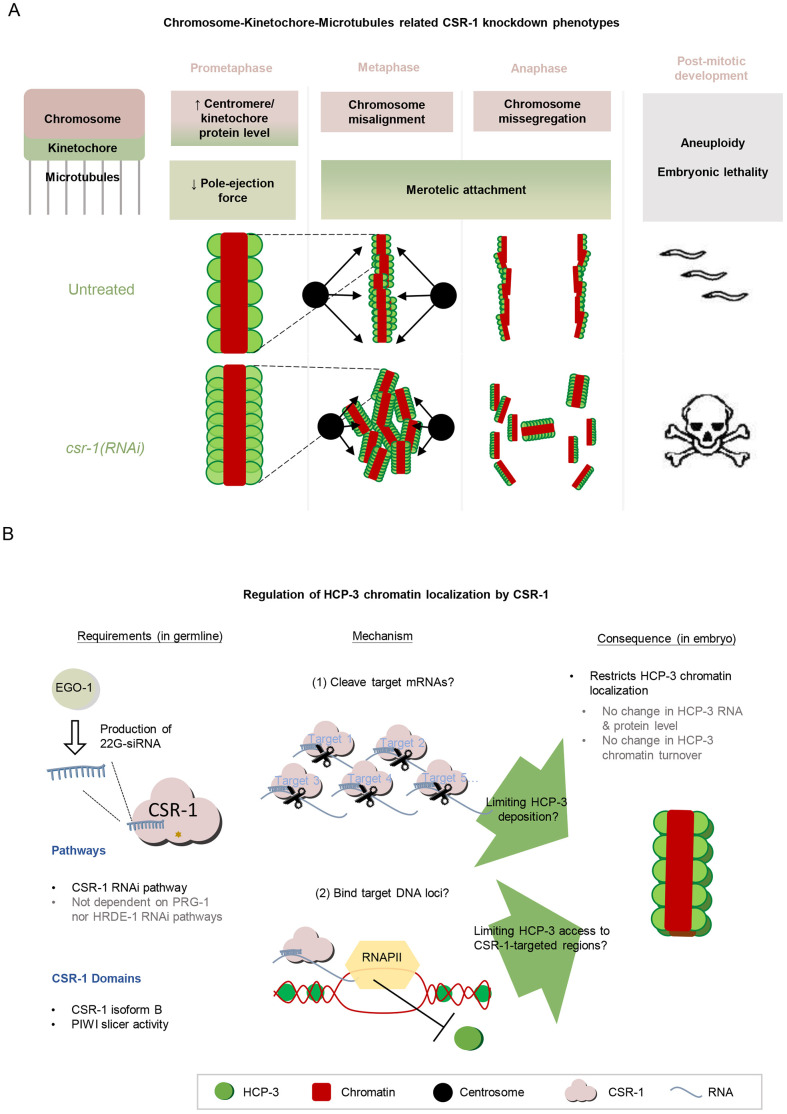
Fig. 7.
Chromosome segregation defects in mitosis upon CSR-1 knockdown and summary of how CSR-1 can repress HCP-3 localization on centromeres. (A) A summary of CSR-1 knockdown phenotypes related to chromosome segregation in mitosis. (B) A proposed mechanism for how CSR-1 affects HCP-3 centromere localization. The germline-enriched CSR-1 isoform B with its PIWI domain is important for regulating embryonic HCP-3 loading onto chromatin. This could be achieved by regulating (1) the level of a target or a subset of mRNA targets by cleaving mRNA, as proposed previously (Gerson-Gurwitz et al., 2016) or (2) an epigenetic mark inhibitory for HCP-3 loading on the target genome via physical interaction with the chromatin in an RNA polymerase II (RNAPII)-dependent manner, as has previously been proposed (Wedeles et al., 2013b). Pathways and CSR-1 domains found to be important for HCP-3 repression are summarized.