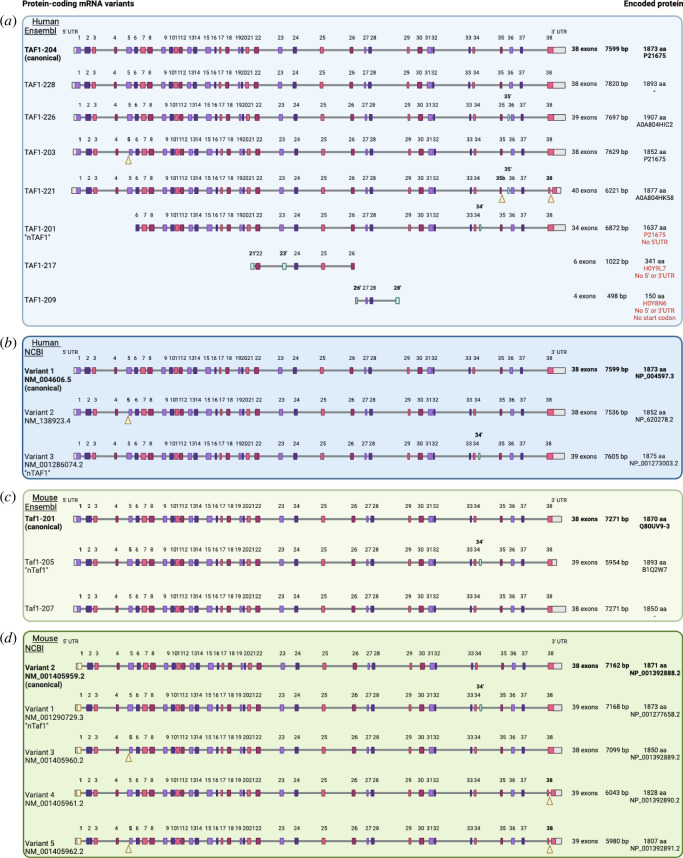
Figure 3.
Genomic architecture (exon–intron structure) of protein-coding mRNA variants for human and mouse TAF1. (a) Eight protein-coding variants are shown for human TAF1 as described in Ensembl and (b) three are defined by NCBI. (c) Three protein-coding variants are shown for mouse Taf1 as categorized by Ensembl and (d) five are categorized by NCBI. The canonical variant (cTAF1/cTaf1; bold) and nTAF1/nTaf1 are indicated. Exons are shown as coloured boxes and introns as grey lines. Grey boxes indicate 5′- and 3′-UTRs. Blue boxes indicate additional exons to the human canonical TAF1 variant. The total number of exons, amino acid (aa) length, and their amino acid translation by UniProt ID are shown on the right. Yellow arrowheads and bold writing on exon number indicate the absence of nucleotides in exons compared with the same exons in the Ensembl canonical variant of respective human or mouse TAF1; yellow boxes and bold writing on exon number indicates sequence variation in exons to the respective human or mouse canonical TAF1 variant. Red writing of UniProt ID indicates that mRNA is unlikely to be translated to protein owing to missing structural features of a complete open reading frame as indicated. Created with BioRender.com.