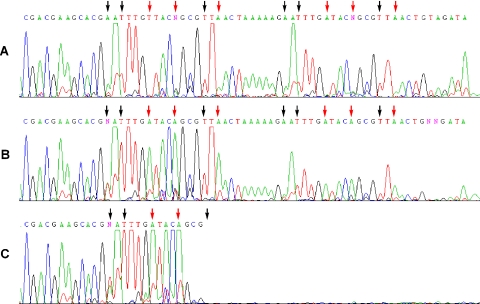
Figure 3.
Dye terminator sequencing (BigDye 3.1 kit) of an ODN containing dMeisoC and disoG used to optimize concentrations of dMeisoCTP and disoGTP. The template sequence in the region shown is 3′-GCTGCTTCGTGCiGTiGAACiCATGiCCGCiGAiC TGATTTTTCiGTiGAACiCATGiCCGCiGAiCTGACATCTA-5′. Changing the concentrations of dMeisoCTP and disoGTP caused differences in dye terminator signals at template disoG (black arrow) and dMeisoC (red arrow) positions. With increasing concentrations of dMeisoCTP, signals from ddT were suppressed opposite template disoG positions. With increasing concentrations of disoGTP, signals from ddA were suppressed opposite dMeisoC template positions. These changes are indicative of competition for incorporation at non-natural template positions between a non-natural nucleotide and a specific natural nucleotide. (A) Sequencing with 100 μM dMeisoCTP and 400 μM disoGTP largely suppressed terminator incorporation opposite the non-natural positions. Modest signal attenuation caused by unwanted strand termination was apparent. (B) As the concentrations of disoGTP and dMeisoCTP were decreased (10 μM dMeisoCTP and 10 μM disoGTP), ddA terminators were incorporated opposite template dMeisoC positions and ddT terminators were incorporated opposite template disoG positions. Signal attenuation caused by unwanted strand termination was increased. (C) In the absence of disoGTP and dMeisoCTP, more ddA was incorporated opposite template disoC and more ddT was incorporated opposite template dMeisoG. Forced misincorporation at all non-natural template positions led to premature termination of the sequencing reaction, unlike in (A) and (B) where it was possible to incorporate some non-natural nucleotide. Similar reactions were performed using the BigDye 3.0 kit (Supplementary Figures S4 and S5).