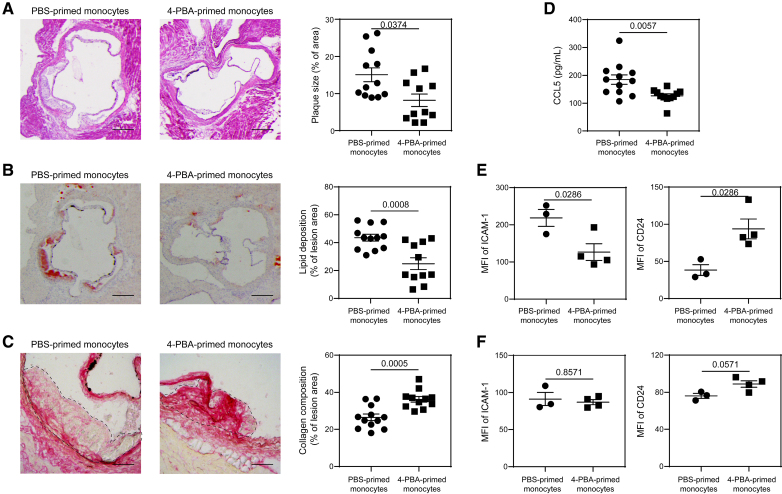
Figure 7.
Adoptive transfer of monocytes polarized by 4-phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA) alleviates atherosclerosis. A through D, Male ApoE−/− mice, serving as recipients, were fed with high-fat diet (HFD) for 4 weeks. Bone marrow–derived monocytes (BMMs) from ApoE−/− mice were treated with PBS or 4-PBA (1 mmol/L) for 5 days. PBS- or 4-PBA-polarized monocytes (3×106 cells per mouse) were then adoptively transferred by intravenous injection to HFD-fed ApoE−/− mice once a week for 4 weeks. Tissues were harvested 1 week after the last monocyte transfer. A, Representative images of H&E-stained atherosclerotic lesions and quantification of plaque size demonstrated as the percentage of lesion area within aortic root area. Scale bars, 300 µm. B, Representative images of oil red O–stained atherosclerotic plaques and quantification of lipid deposition within lesion area. Scale bars, 300 µm. C, Representative images of Picrosirius red–stained atherosclerotic plaques and quantification of collagen content within lesion area. Scale bars, 100 µm. D, Detection of chemokine ligand 5 (CCL5) level in the plasma by ELISA. E and F, PBS- or 4-PBA-polarized monocytes were labeled with CFSE immediately before adoptive transfer, and tissues were harvested 1 week after the last monocyte transfer. Surface expressions of ICAM-1 and CD24 on host CFSE− CD11b+ Ly6G− Ly6Chi monocytes in the aorta (E) and bone marrow (BM; F) were determined by flow cytometry. Data in A, E, and F were analyzed using Mann-Whitney U test, and data in B through D were analyzed using Student t test (n=12 for PBS-trained monocytes group and n=11 for 4-PBA–trained monocytes group in A through D; n=3 for PBS-trained monocytes group and n=4 for 4-PBA-trained monocytes group in E and F; biological replicates). Error bars represent means±SEM.