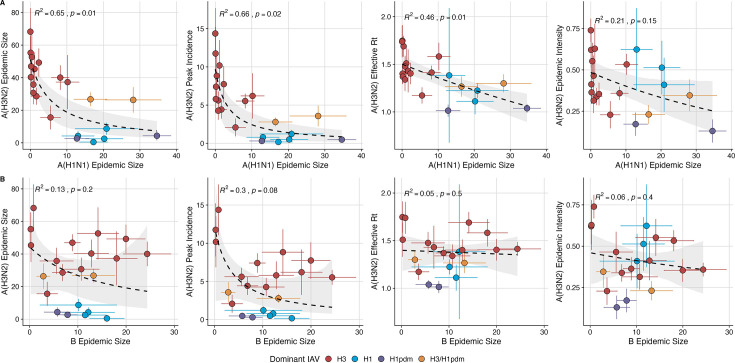
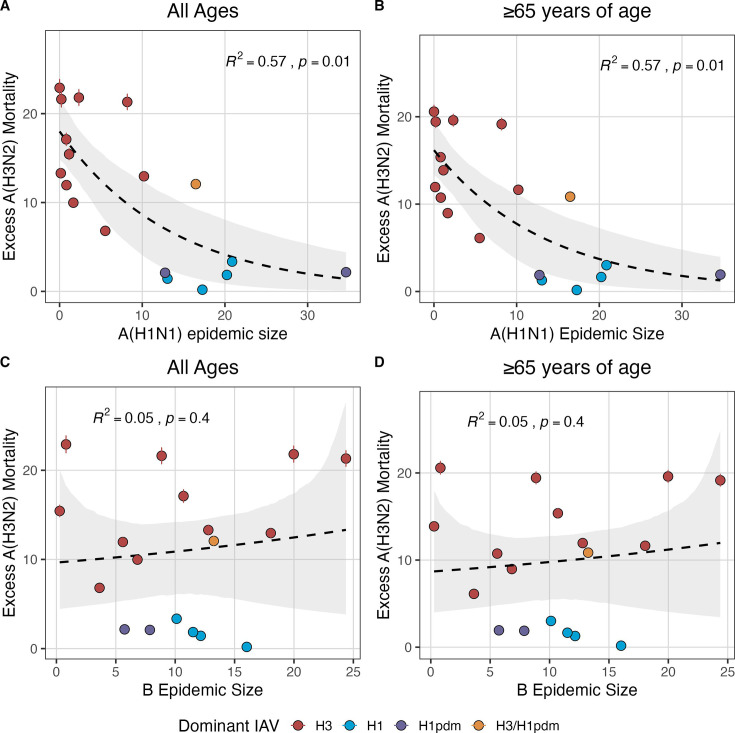
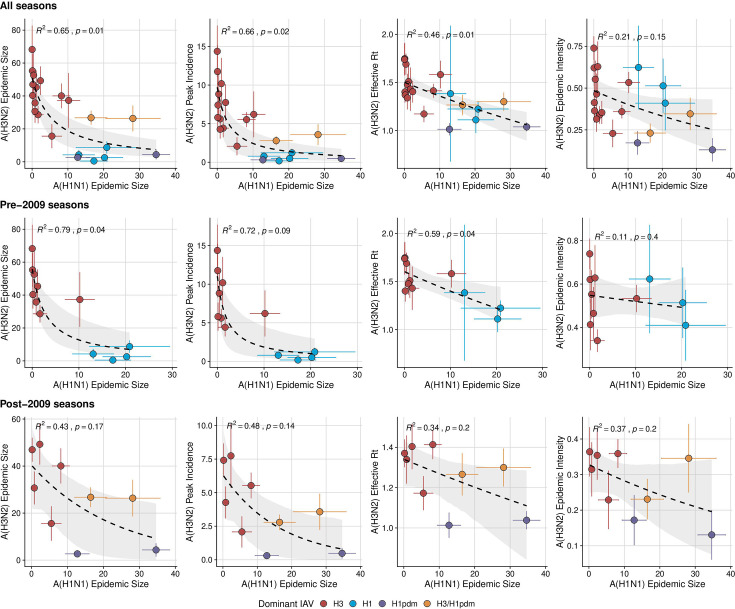
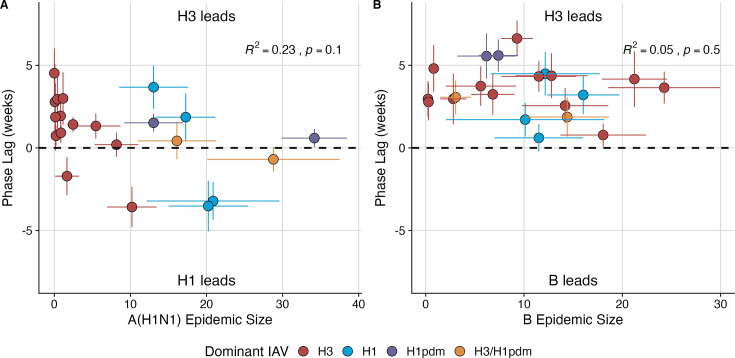
Figure 7. The effects of influenza A(H1N1) and B epidemic size on A(H3N2) epidemic burden.
(A) Influenza A(H1N1) epidemic size negatively correlates with A(H3N2) epidemic size, peak incidence, transmissibility (effective reproduction number, ), and epidemic intensity. (B) Influenza B epidemic size does not significantly correlate with A(H3N2) epidemic metrics. Point color indicates the dominant influenza A virus (IAV) subtype based on CDC influenza season summary reports (red: A(H3N2), blue: A(H1N1), purple: A(H1N1)pdm09, orange: A(H3N2)/A(H1N1)pdm09 co-dominant), and vertical and horizontal bars are 95% confidence intervals of regional estimates (pre-2009 seasons: 9 regions; post-2009 seasons: 10 regions). Seasonal mean A(H3N2) epidemic metrics were fit as a function of mean A(H1N1) or B epidemic size using Gaussian GLMs (epidemic size and peak incidence: inverse link; effective : log link) or Beta GLMs (epidemic intensity: logit link) with 1000 bootstrap resamples. In each plot, the black dashed line represents the mean regression fit, and the gray shaded band shows the 95% confidence interval, based on 1000 bootstrap resamples. The R2 and associated p-value from the mean regression fit are in the top left section of each plot.