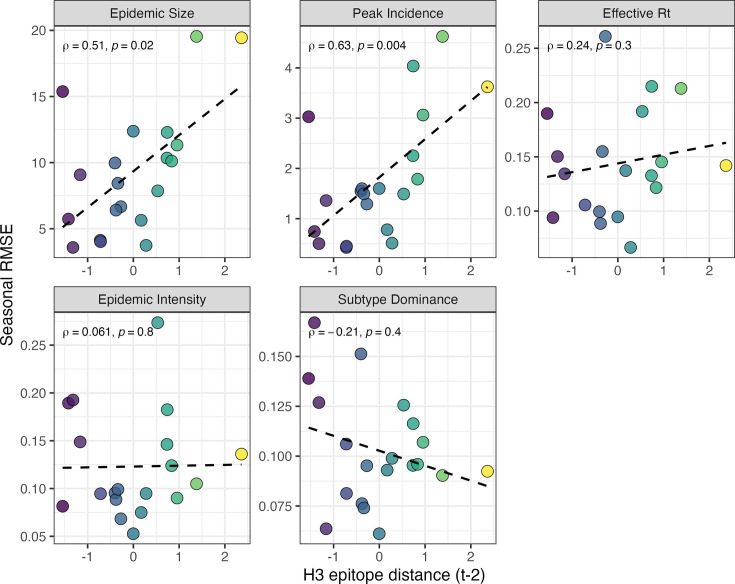
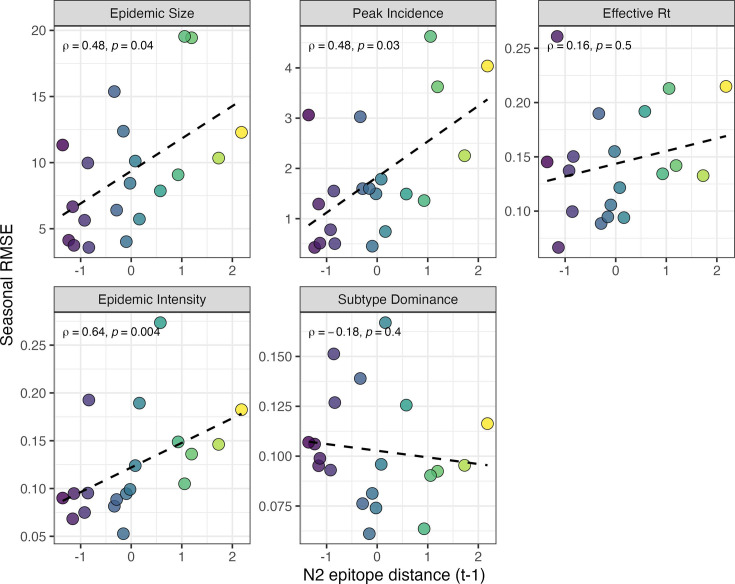
Figure 9. Observed versus predicted values of seasonal region-specific influenza A(H3N2) epidemic metrics from conditional inference random forest models.
(A) Epidemic size, (B) peak incidence, (C) transmissibility (maximum effective reproduction number, ), (D) epidemic intensity, and (E) subtype dominance. Results are facetted by HHS region and epidemic metric. Point color and size corresponds to the mean H3 epitope distance between viruses circulating in the current season and viruses circulating two prior seasons ago ( – 2). Large, yellow points indicate seasons with high antigenic novelty, and small blue points indicate seasons with low antigenic novelty. In each facet, the Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient and associated p-value are in the top left section, and the black dashed line shows .