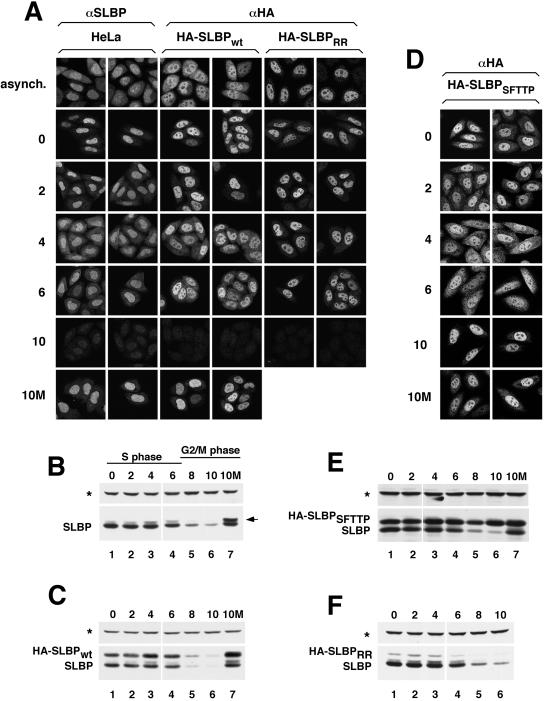
Figure 2.
Subcellular distribution of SLBP changes during S phase and is dependent on RNA binding. (A) Untransfected HeLa cells (left two columns), a clonal cell line expressing HA-SLBPwt (center two columns) or a pool of stably transfected cells expressing HA-SLBPRR (right two columns) were synchronized by double-thymidine block. After release from the second thymidine block, the localization of the endogenous SLBP (left two columns) or HA-tagged SLBPs (remaining four columns) was monitored every 2 h by immunostaining with either the anti-SLBP or anti-HA antibody. The top row shows the localization of the various SLBPs in an asynchronous population of cells and the remaining rows show cells at different times (hours) after release from double thymidine block. The bottom row shows the localization of the endogenous SLBP and HA-SLBPwt in cells exposed to MG132 at 4 h (S phase) and harvested 10 h (G2 phase) after release (10M). (B and C) Western blot by using the anti-SLBP antibody to illustrate the expression profile of the endogenous SLBP (B) and HA-SLBPwt (C) in the same cells as those shown in A. The asterisk marks the 75-kDa protein that cross-reacts with the SLBP antibody on Western blots. The arrow indicates the phosphorylated SLBP, which accumulates when protein degradation is blocked at the end of S phase. (D) A clonal cell line expressing HA-SLBPSFTTP was synchronized, and the localization of HA-SLBPSFTTP was determined using the anti-HA antibody as in A. (E and F) Lysates prepared from HA-SLBPSFTTP (E) or HA-SLBPRR (panel F) expressing cells (at the indicated times postrelease from double-thymidine block) were tested for SLBP levels by Western blot analysis by using the SLBP antibody.