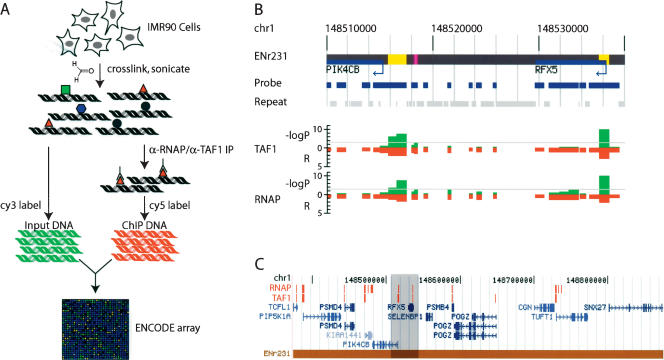
Figure 1.
Direct isolation and identification of promoters in the human genome. (A) A schematic of GWLA for mapping RNAP and TAF1-binding sites. Growing cells are cross-linked with formaldehyde, and their nuclei are isolated and sonicated. The resulting chromatin (protein-DNA) complexes are incubated with either anti-RNAP (α-RNAP) or anti-TAF1 (α-TAF1) antibody. The immunoprecipitated DNA is subjected to ligation-mediated PCR, labeled with Cy5 dye, and competitively hybridized to the ENCODE array (described in Supplemental materials) with the Cy3-labeled unenriched chromatin (Li et al. 2003). (B) A typical detailed view of the TAF1- and RNAP-binding data (within the ENCODE region, ENr231). Negative logarithmic P values of enrichment by RNAP or TAF1 ChIP for each probe are plotted in green. Relative enrichment (R) values by RNAP or TAF1 ChIP for each probe fragment are plotted in red on the inverted axis. (C) A representative view of an entire ENCODE locus (ENr231) with annotated RNAP- and TAF1-binding sites that have P values <0.0001, noted in red blocks (The detailed view in B is highlighted in gray).