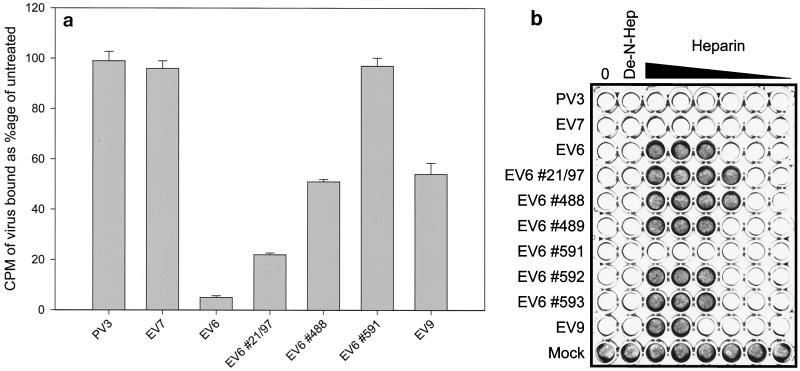
FIG. 2.
Heparin inhibits the binding (a) and infection (b) of RD cells by EV6. (a) Binding of radiolabeled EV6, clinical isolates of EV6 (indicated by the number symbol), EV7, EV9, and PV3 to RD cells was monitored in the presence of 1 mg of heparin/ml. Results are presented as the percentage of virus bound in comparison to binding of the untreated virus control (mean and standard deviation). (b) The inhibitory effect of heparin on infection of RD cells was determined by preincubating 1,000 TCID50 of the indicated viruses with dilutions of heparin (doubling dilutions from 2 mg/ml to 62.5 ng/ml) for 15 min before addition to 80% confluent RD cells. Infection was determined by staining with crystal violet after 24 h. The row labeled “Mock” indicates the effect of heparin in the absence of virus; lanes labeled 0 and De-N-Hep contained no heparin or 1 mg of de-N-sulfated heparin/ml, respectively.