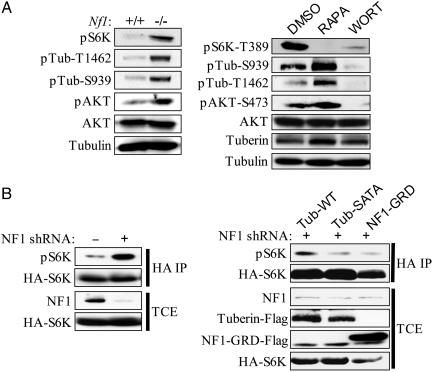
Fig. 3.
Hyperactivation of the PI3 kinase pathway in Nf1-/- primary MEFs results in tuberin inactivation. (A Left) Western blot analysis of serum-starved Nf1+/+ and Nf1-/- MEFs. Abbreviations are as follows: pS6K, p70S6K phosphorylated at T389; pAKT, AKT phosphorylated at S473; pTub-T1462, tuberin phosphorylated at T1462; pTub-S939, tuberin phosphorylated at S939. (A Right) Western blot analysis of tuberin phosphorylation in serum-starved Nf1-/- MEFs after treatment with DMSO, rapamycin, or wortmannin. (B Left) HEK293 cells expressing either pLKO lentiviral vector or a short hairpin RNA (shRNA) against NF1 were transfected with an hemagglutinin-tagged p70S6K reporter. (B Right) HEK293 cells expressing shRNA against NF1 were transfected with the indicated tuberin or NF1-GRD constructs along with a hemagglutinin-tagged p70S6K reporter. Abbreviations are as follows: Tub-WT, wild-type tuberin; Tub-SATA, tuberin with alanine mutations at the AKT phosphorylation sites S939/T1462. Hemagglutinin immunoprecipitates (HA IP) and total cell extracts (TCE) were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.