Figure 3.
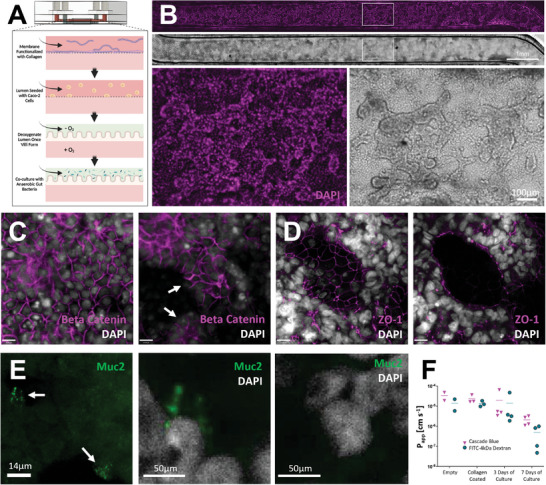
Characterization of polycarbonate gut chips. A) Schematic overview of gut microbiome assembly on chip. Channels are functionalized with collagen prior to Caco‐2 cell seeding. Following growth of villus‐like structures, gut lumen channel media is depleted of oxygen for co‐culture with anaerobic gut microbes; B) Gut chip channel with Caco‐2 cells grown into villus‐like structures, shown in brightfield and with nuclei stained by DAPI (magenta), scale bar denotes 1 mm; C) Immunofluorescence imaging of polarized Caco‐2 layers on day 7 using markers DAPI (greyscale) and anti‐Beta Catenin (magenta) show basolateral staining of beta catenin at intercellular junctions (left) and no staining at apical surfaces (right). Arrows indicate examples of apical surfaces devoid of beta catenin staining, scale bars denote 14 µm; D) Caco‐2 barriers characterized by immunofluorescence imaging of tight junction protein ZO‐1 (magenta) and DAPI (grayscale), shown here on day 9, show ZO‐1 expression at cellular interfaces (left) and apical to nuclei at the villus surface (right), scale bars denote 14 µm; E) A subset of Caco‐2 cells transdifferentiate into goblet‐like cells producing mucin, noted by arrows, shown here on day 9 (left), a pullout shows a cell staining positively for Muc2 (middle), cells without Muc2 staining (right); F) Permeability data of gut chips from initial assembly through seven days of culture tracking Cascade Blue hydrazide and FITC‐dextran 4 kDa.
