Figure 2.
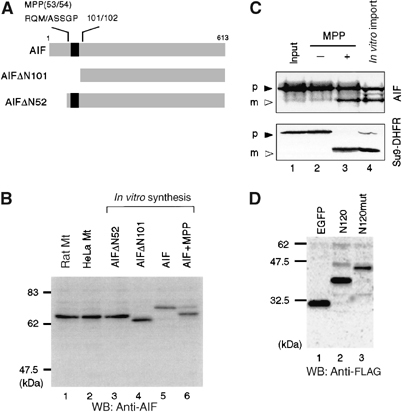
Determination of the processing site of AIF precursor during mitochondrial import. (A) Schematic representation of AIF and its truncation mutants. Numbers represent the positions in the AIF precursor amino-acid sequence. Predicted TMS is shown in black boxes and apoptosis-dependent processing site (101/102) is indicated on the top of the figure. The MPP-processed site deduced by N-terminal sequencing is shown. (B) N-terminal segment of ∼50 amino-acid residues is cleaved by MPP. Mitochondria from rat liver and HeLa cells, cell-free synthesized AIFΔN52, AIFΔN101, and full-length AIF, and cell-free synthesized full-length AIF precursor that had been incubated with purified MPP were subjected to SDS–PAGE and subsequent immunoblot analysis using anti-AIF antibodies. (C) In vitro-synthesized 35S-labeled AIF precursor and pSu9-DHFR (lane 1) were incubated with or without purified MPP (lanes 2 and 3, respectively) or with isolated rat liver mitochondria (lane 4). The reaction mixtures were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and autoradiography. Solid and open arrowheads represent precursor proteins (p) and mature proteins (m), respectively. (D) The MPP-processing site of AIF was probed using the alanine-substituted mutant. N120-GFP-FLAG (N120) and the mutant carrying R51A-M53-A-S55/56A mutations (N120mut) were expressed in HeLa cells and the lysates were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting using anti-FLAG antibody.
