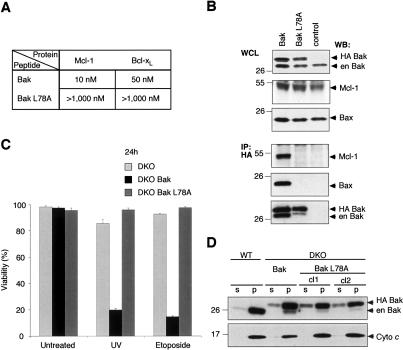
Figure 4.
Bak BH3 is required for interaction with Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL, and for proapoptotic function. (A) A point mutation within Bak BH3 abrogates interaction with Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL. Using solution competition assays, the relative affinities (IC50 in nanomolar) of Bak and mutant Bak L78A peptides for Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL were determined. (B) Bak L78A fails to heterodimerize with Mcl-1 or homodimerize. N-terminally HA-tagged wild-type Bak or mutant Bak L78A were transiently expressed in 293T cells (top) and tested for their ability to bind endogenous Mcl-1, Bax or Bak (bottom) by coimmunopreciptation using anti-HA affinity resin. (Control) Immunoprecipitation from untransfected cells; (en) endogenous. (C) L78A mutation inactivates Bak proapoptotic function. Viability was determined for Bax/Bak-deficient (DKO) MEFs or ones containing introduced Bak or Bak L78A, left untreated or 24 h after UV or etoposide treatment. Data represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments. (D) L78A mutant Bak, like wild-type Bak, localizes to the pellet fraction. Wild-type MEFs or Bax/Bak-deficient ones expressing wild-type Bak or mutant Bak L78A (two independent clones) were fractionated (in digitonin-containing buffer) into soluble (s) and pellet (p) fractions, and probed for Bak (top) or cytochrome c (bottom).