Figure 6.
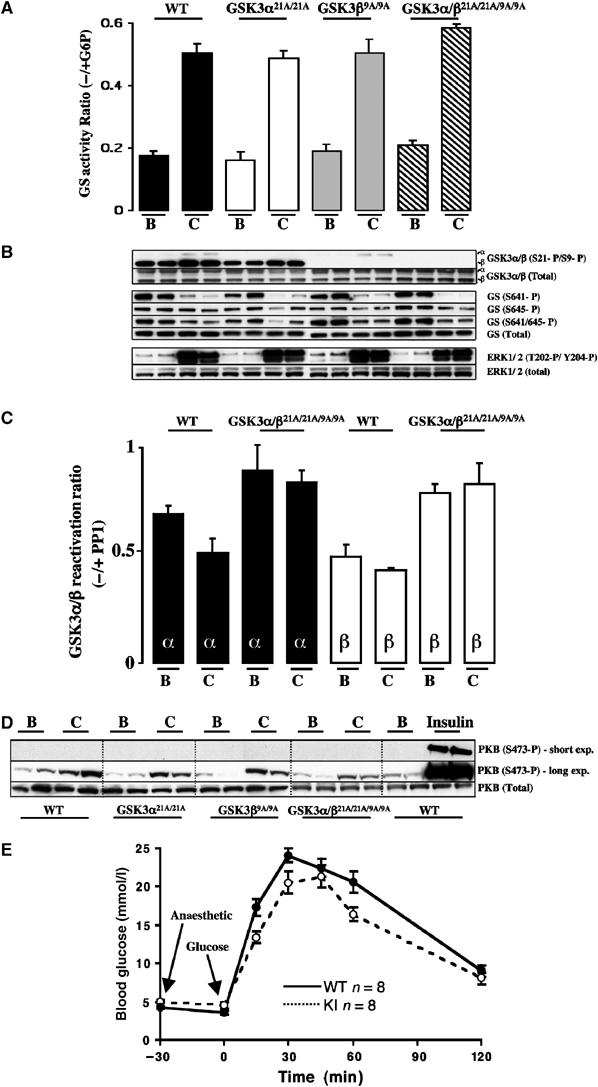
Effect of muscle contraction on glycogen synthase and glucose tolerance in the knockin mice. (A) One leg from anaesthetised WT and knockin mouse was subjected to in situ hindlimb muscle contraction (C, contraction) via sciatic nerve stimulation for 10 min, and the other leg served as noncontracted control (B, basal). Red and white gastrocnemius and extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscles from both legs were rapidly extracted and snap frozen in liquid nitrogen. Glycogen synthase activity was measured in the absence and presence of G6P. The data are presented as the mean±s.e.m. for muscle isolated from four mice each assayed ±G6P in duplicate. (B) Muscle extracts from the indicated mice were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. As for Figure 2, only the WT controls for the GSK3α21A/21A are shown. (C) GSK3α and GSK3β were immunoprecipitated from WT and double knockin GSK3 muscle derived from (A), and activity was measured as a ratio of ±treatment with PP1γ phosphatase as described in Materials and methods. The data are presented as the mean±s.e.m. for muscle isolated from two mice, each assayed in triplicate. (D) Muscle extracts from the WT and knockin mice were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. The insulin-treated samples were derived from the muscle of mice that had been injected with insulin as described in Figure 2. In order to compare the levels of phosphorylation of PKB seen in response to insulin and muscle contraction, a short and long exposure of the immunoblot is shown. (E) The indicated mice were fasted overnight and blood glucose levels measured. The mice were then anaesthetised and after 30 min a glucose tolerance test was carried out after mice were injected intraperitoneally with 2 mg/g glucose solution and the blood glucose concentration was determined at the indicated times. n indicates the number of mice in each group. The data are presented as the mean±s.e.m. and similar numbers of female and male mice were present in each group.
