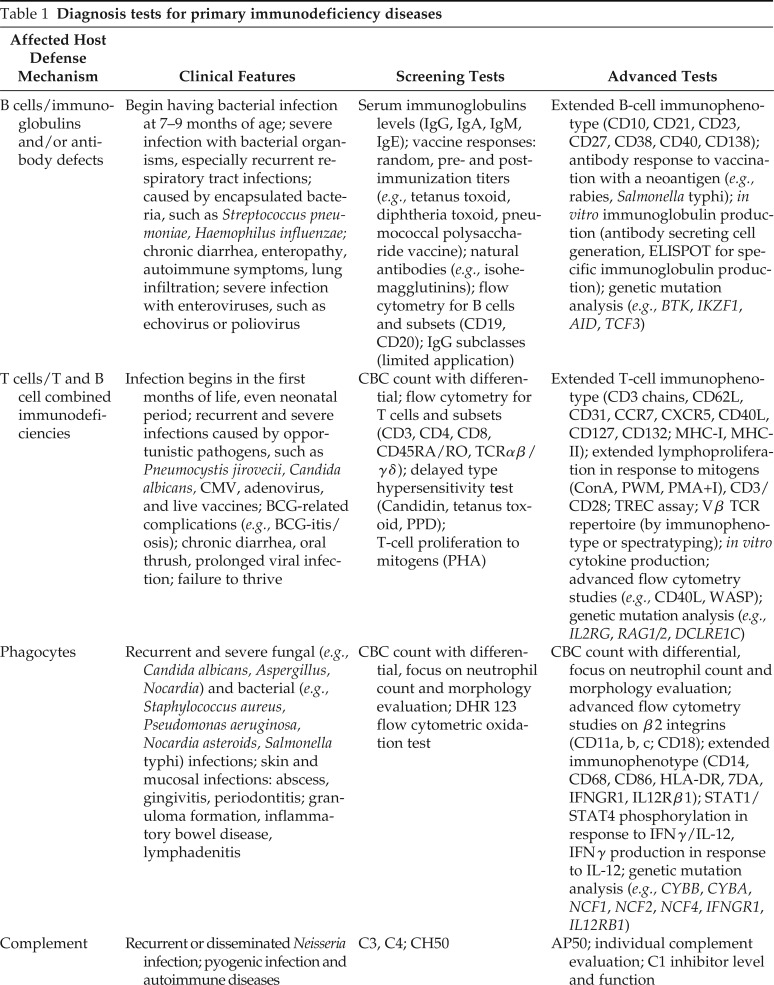
Table 1.
Diagnosis tests for primary immunodeficiency diseases
| Affected Host Defense Mechanism | Clinical Features | Screening Tests | Advanced Tests |
|---|---|---|---|
| B cells/immunoglobulins and/or antibody defects | Begin having bacterial infection at 7–9 months of age; severe infection with bacterial organisms, especially recurrent respiratory tract infections; caused by encapsulated bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae; chronic diarrhea, enteropathy, autoimmune symptoms, lung infiltration; severe infection with enteroviruses, such as echovirus or poliovirus | Serum immunoglobulins levels (IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE); vaccine responses: random, pre- and postimmunization titers (e.g., tetanus toxoid, diphtheria toxoid, pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine); natural antibodies (e.g., isohemagglutinins); flow cytometry for B cells and subsets (CD19, CD20); IgG subclasses (limited application) | Extended B-cell immunophenotype (CD10, CD21, CD23, CD27, CD38, CD40, CD138); antibody response to vaccination with a neoantigen (e.g., rabies, Salmonella typhi); in vitro immunoglobulin production (antibody secreting cell generation, ELISPOT for specific immunoglobulin production); genetic mutation analysis (e.g., BTK, IKZF1, AID, TCF3) |
| T cells/T and B cell combined immunodeficiencies | Infection begins in the first months of life, even neonatal period; recurrent and severe infections caused by opportunistic pathogens, such as Pneumocystis jirovecii, Candida albicans, CMV, adenovirus, and live vaccines; BCG-related complications (e.g., BCG-itis/osis); chronic diarrhea, oral thrush, prolonged viral infection; failure to thrive | CBC count with differential; flow cytometry for T cells and subsets (CD3, CD4, CD8, CD45RA/RO, TCRαβ/γδ); delayed type hypersensitivity test (Candidin, tetanus toxoid, PPD); T-cell proliferation to mitogens (PHA) | Extended T-cell immunophenotype (CD3 chains, CD62L, CD31, CCR7, CXCR5, CD40L, CD127, CD132; MHC-I, MHC-II); extended lymphoproliferation in response to mitogens (ConA, PWM, PMA+I), CD3/CD28; TREC assay; Vβ TCR repertoire (by immunophenotype or spectratyping); in vitro cytokine production; advanced flow cytometry studies (e.g., CD40L, WASP); genetic mutation analysis (e.g., IL2RG, RAG1/2, DCLRE1C) |
| Phagocytes | Recurrent and severe fungal (e.g., Candida albicans, Aspergillus, Nocardia) and bacterial (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Nocardia asteroids, Salmonella typhi) infections; skin and mucosal infections: abscess, gingivitis, periodontitis; granuloma formation, inflammatory bowel disease, lymphadenitis | CBC count with differential, focus on neutrophil count and morphology evaluation; DHR 123 flow cytometric oxidation test | CBC count with differential, focus on neutrophil count and morphology evaluation; advanced flow cytometry studies on β2 integrins (CD11a, b, c; CD18); extended immunophenotype (CD14, CD68, CD86, HLA-DR, 7DA, IFNGR1, IL12Rβ1); STAT1/STAT4 phosphorylation in response to IFNγ/IL-12, IFNγ production in response to IL-12; genetic mutation analysis (e.g., CYBB, CYBA, NCF1, NCF2, NCF4, IFNGR1, IL12RB1) |
| Complement | Recurrent or disseminated Neisseria infection; pyogenic infection and autoimmune diseases | C3, C4; CH50 | AP50; individual complement evaluation; C1 inhibitor level and function |
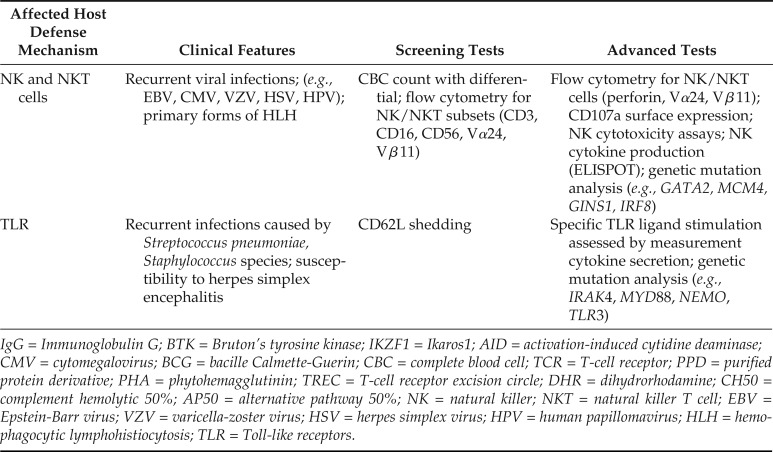
| NK and NKT cells | Recurrent viral infections; (e.g., EBV, CMV, VZV, HSV, HPV); primary forms of HLH | CBC count with differential; flow cytometry for NK/NKT subsets (CD3, CD16, CD56, Vα24, Vβ11) | Flow cytometry for NK/NKT cells (perforin, Vα24, Vβ11); CD107a surface expression; NK cytotoxicity assays; NK cytokine production (ELISPOT); genetic mutation analysis (e.g., GATA2, MCM4, GINS1, IRF8) |
| TLR | Recurrent infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus species; susceptibility to herpes simplex encephalitis | CD62L shedding | Specific TLR ligand stimulation assessed by measurement cytokine secretion; genetic mutation analysis (e.g., IRAK4, MYD88, NEMO, TLR3) |
IgG = Immunoglobulin G; BTK = Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; IKZF1 = Ikaros1; AID = activation-induced cytidine deaminase; CMV = cytomegalovirus; BCG = bacille Calmette-Guerin; CBC = complete blood cell; TCR = T-cell receptor; PPD = purified protein derivative; PHA = phytohemagglutinin; TREC = T-cell receptor excision circle; DHR = dihydrorhodamine; CH50 = complement hemolytic 50%; AP50 = alternative pathway 50%; NK = natural killer; NKT = natural killer T cell; EBV = Epstein-Barr virus; VZV = varicella-zoster virus; HSV = herpes simplex virus; HPV = human papillomavirus; HLH = hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; TLR = Toll-like receptors.