Figure 1.
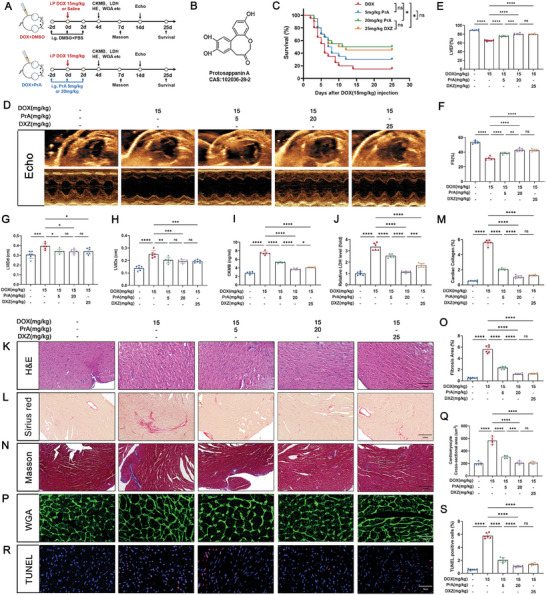
PrA alleviates DOX‐induced cardiac injury. A) Schematic diagram of animal experiment process. Briefly, mice were treated with PrA (5 or 20 mg kg−1, i.g.), DXZ (an iron chelating agent, 25 mg kg−1, i.p.) or DMSO with PBS on day 0, day 2, and day 4, followed by DOX (20 mg kg−1, i.p.) on day 2, while mice were injected with saline only as a control treatment on day 2. B) The chemical structure of the PrA. C) Kaplan‐Meier survival curves of mice in each group (n = 20 per group). D) Representative echocardiographic images showing the cardiac function of mice in each group. E–H) Quantitative analysis of LVEF, FS, LVIDd, and LVIDs (n = 6 per group). I,J) Serum CK‐MB (fivefold dilution) and LDH levels were measured in each group (n = 6 per group). K) Representative images of H&E staining (n = 6 per group, scale bar = 100 µm). L,M) Representative images and quantitative analysis of Sirius red staining (n = 6 per group, scale bar = 100 µm). N,O) Representative images and quantitative analysis of Masson's trichrome staining (n = 6 per group, scale bar = 100 µm). P) Representative images and Q) quantitative analysis of WGA staining (n = 6 per group, scale bar = 20 µm). R) Representative images and S) quantitative analysis of TUNEL staining (n = 6 per group, scale bar = 20 µm). The data presented in panel J was normalized. Summary data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated using C) the log‐rank (Mantel‐Cox) test and E–J,K,M,O, Q,S) one‐way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Abbreviations: CK‐MB, creatine kinase‐MB; DMSO, dimethylsulfoxide; DOX, doxorubicin; DXZ, dexrazoxane; FS, left ventricular fractional shortening; i.g., intragastric; i.p., intraperitoneal; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; LVIDd, left ventricular internal dimension in diastole; LVIDs, left ventricular internal dimension in systole; PBS, phosphate buffer saline; PrA, protosappanin A.
