Figure 1.
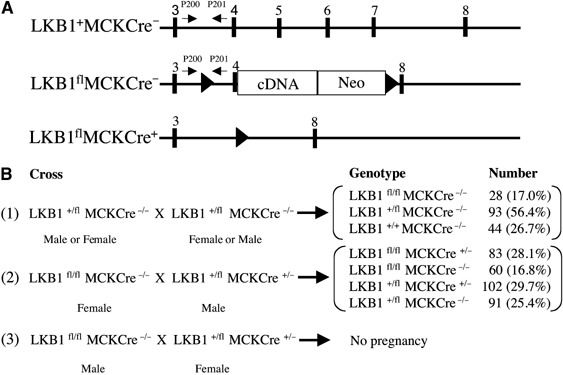
Generation of LKB1-deficient mice. (A) Diagram illustrating the positions of exons 3–8 (▪) in the wild-type LKB1+Cre− allele. In the LKB1flCre− allele, exon 4 of the LKB1 gene is flanked with loxP Cre recombinase excision sites (▴), and exons 5–7 encoding the catalytic domain of LKB1 are replaced with a cDNA construct encoding the remainder of the LKB1 sequence, as well as a neomycin (Neo) selection gene. The expression of the neomycin gene is driven by the LKB1 promoter and it is made as fusion mRNA with LKB1. Its translation is directed by an internal ribosome entry site. In the LKB1flCre+ allele, exons 4–7 of the LKB1 gene are deleted through action of the Cre recombinase, thereby ablating functional expression of LKB1. The positions of the PCR primers used to genotype the mice are indicated with arrows. (B) Breeding strategy employed to generate LKB1fl/fl and LKB1-muscle-deficient (LKB1fl/flCre+/−) mice, where MCKCre denotes transgenic mice expressing the Cre recombinase under the muscle creatine kinase promoter. The number and percentage of each genotype obtained are indicated.
