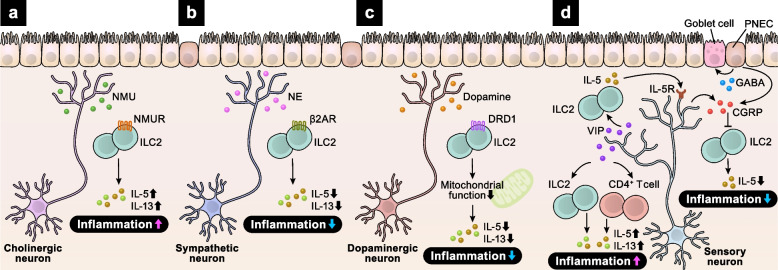
Fig. 2.
Neuro–immune crosstalk in the lung. a–d Upon allergen exposure, various types of neurons activate immune responses in the lung.Cholinergic neuron-derived NMU induces IL-5 and IL-13 secretion from ILC2s via NMUR, exaggerating lung inflammation (a). NE from sympathetic neurons and dopamine from dopaminergic neurons inhibit ILC2 responses via β2AR (b) and DRD1 (c), respectively. Sensory neuron-derived VIP activates ILC2s and CD4+ T cells to produce IL-5 and IL-13, which exacerbates allergic inflammation. In turn, ILC2-derived IL-5 binds to IL-5R on sensory neurons and promotes CGRP secretion. CGRP, derived from both sensory neurons and PNECs, inhibits ILC2 responses and suppresses airway inflammation (d)