Figure 3.
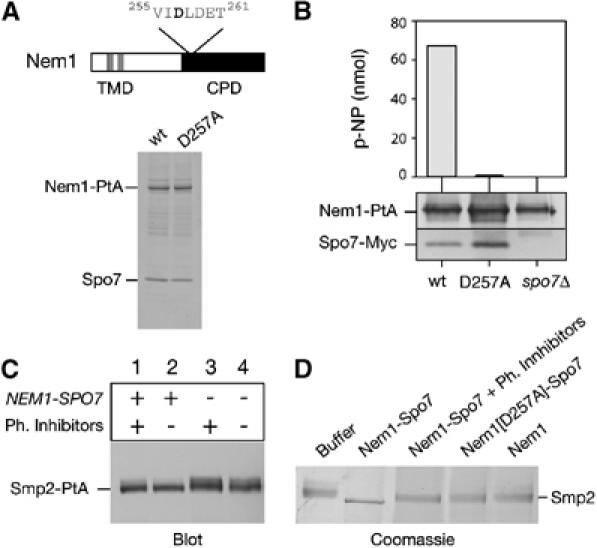
Dephosphorylation of Smp2 by the Nem1–Spo7 complex. (A) Upper panel: domain organization of Nem1. TMD, transmembrane domain. CPD, CTD Phosphatase domain. The DLD phosphoacceptor site is indicated. Lower panel: affinity purification of Nem1-PtA (‘wt') and Nem1[D257A]-PtA (‘D257A'). Purified proteins were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and Coomassie staining. The positions of the PtA-fusions and copurifying Spo7 are indicated. (B) The Nem1–Spo7 complex exhibits phosphatase activity in vitro. In vitro dephosphorylation of p-nitrophenylphosphate (p-NPP) by the Nem1–Spo7 complex. IgG-Sepharose beads loaded with (Nem1-PtA)–(Spo7-Myc), (Nem1[D257A]-PtA)–(Spo7-Myc) or Nem1-PtA fusions, were tested for the ability to hydrolyze p-NPP as described under Materials and methods. Absorbance of the generated p-nitrophenol (p-NP) was measured at 410 nm. The amount of Nem1 and Spo7 in each reaction was followed by Western blot with anti-PtA and anti-Myc antibodies respectively. (C) Nem1–Spo7 is a phosphatase for Smp2. Protein extracts from smp2Δ (lanes 1 and 2) or nem1Δ spo7Δ smp2Δ (lanes 3 and 4) strains expressing a Smp2-PtA fusion were prepared in the presence (lanes 1 and 3) or absence (lanes 2 and 4) of phosphatase inhibitors. Smp2-PtA was detected by western blot using anti-PtA antibody. (D) In vitro dephosphorylation of Smp2 by the Nem1–Spo7 complex. Native Smp2 (2 μg) was incubated with IgG-Sepharose beads alone (‘buffer') or beads containing the indicated protein A fusions for 30 min at 30°C. Reactions were resolved by 7% SDS–PAGE and Coomassie stained.
