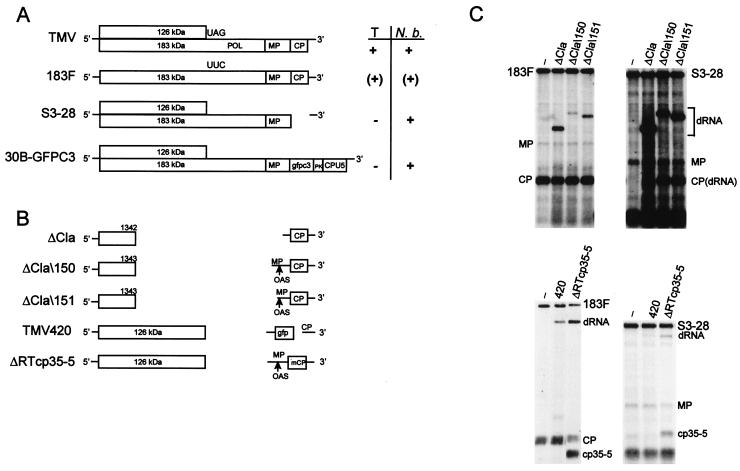
FIG. 1.
(A) Schematic diagram of the genomic organization of TMV-based helper viruses. Locations of POL domain in TMV and stop codon replacement in 183F are indicated. The movement phenotype of helper virus (right) is indicated as follows: +, wt; (+), delayed; −, no long-distance movement. T, tobacco; N. b., N. benthamiana; PK, TMV pseudoknots; CPU5, subgenomic promoter and CP from TMGMV strain U5. (B) Artificially constructed dRNAs of TMV. Boxes, ORFs. Translation products encoded by the respective ORFs are indicated. Lines, nontranslatable sequences; gaps, deleted sequences; mCP, mutated coat protein (cp35–5); gfp, GFP (cycle 3); arrows, retention of complete OAS. (C) Replication of artificially constructed dRNAs in protoplasts. Tobacco suspension cell protoplasts (2 × 106) were transfected with helper virus alone or in combination with a dRNA. Total RNA extracted at 22 h p.i. was analyzed by Northern blot hybridization with a riboprobe complementary to the 3′ untranslated region (20). Positions of helper virus (183F or S3–28) and dRNA genomic RNAs and MP and CP and mutated CP (cp35–5) subgenomic mRNAs are indicated. Lane −, helper virus without dRNA.