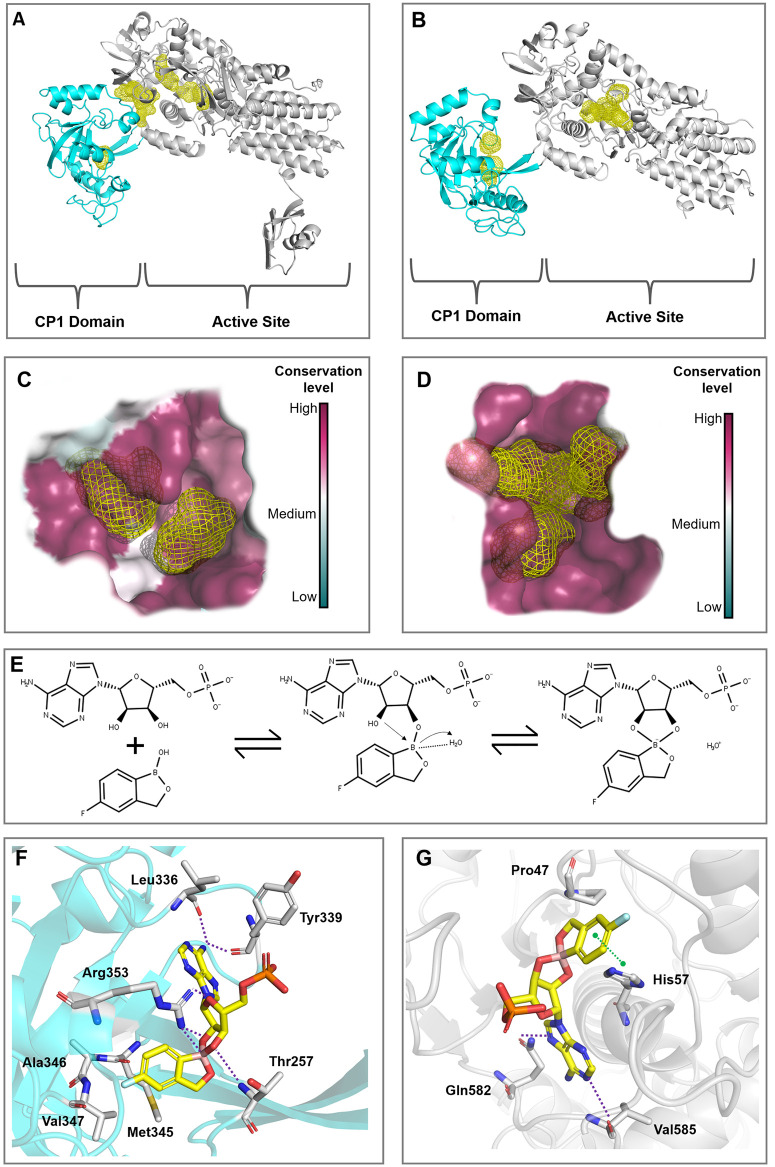
Fig 3. Leucyl-tRNA synthetase structural analysis and molecular docking.
(A) Predicted hot spots (yellow) in the AlphaFold structure. (B) Predicted hot spots (yellow) in the SWISS-MODEL structure. LeuRS’s CP1 and active site domains were highlighted in cyan and gray, respectively. (C) and (D) show the evolutionary conservation level of amino acids around the hot spots in the CP1 domain and in the active site, respectively. (E) Likely tavaborole-inhibition mechanism in LeuRS’s CP1 domain. The boron atom found in tavaborole triggers the attack on the 2’OH of the AMP ribose. Benzoxaborole, at the LeuRS CP1 domain, forms a covalent adduct with AMP by using its boron atom to bind with adenosine 2’ and 3’ oxygen atoms. The boron atom carries a negative charge within the tRNA-AN2690 adduct and achieves stabilization by interacting with a protonated water molecule. (F) and (G) represent tavaborole’s predicted binding modes in LeuRS’ CP1 domain and active site, respectively. Residues interacting with the ligand are shown in gray sticks, whereas the π-π stacking and hydrogen bonds are highlighted in green- and purple-dashed lines, respectively.