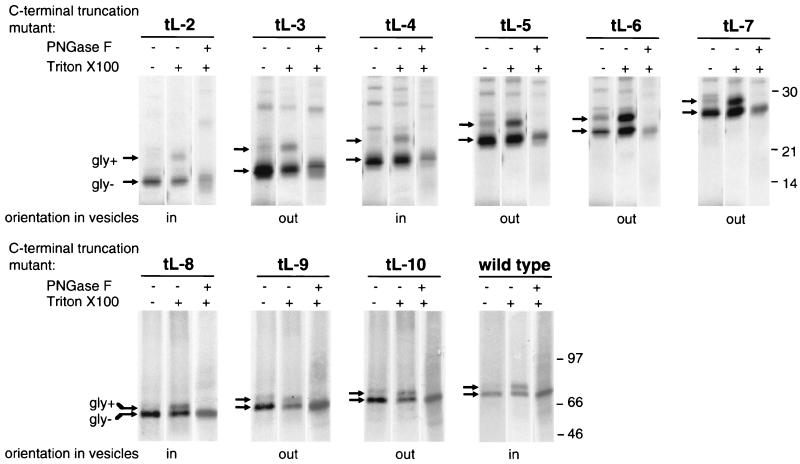
FIG. 4.
Immunoprecipitation of in vitro translation products of human PiT-2 C-terminal-truncation mutants. Plasmids encoding C-terminally truncated forms of human PiT-2 and bearing a C-terminal Myc-His tag were transcribed in vitro, and transcription products were translated in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate assay in the presence of 35S-labeled methionine and cysteine and of microsomal vesicles. Vesicles were then either disrupted by a detergent (Triton X-100) (+) or kept intact (−). A MAb directed against the Myc tag (9E10) was added for 4 h at 4°C, and immune complexes were precipitated by binding to antimouse magnetic beads. After elution from beads, translation products were treated (+) or not treated (−) with PNGase F, an enzyme removing N-linked oligosaccharides. C-terminal truncations were performed at the C-terminal extremities of the predicted L-2, L-3, L-4, L-5, L-6, L-7, L-8, L-9, and L-10 loops (see Materials and Methods and Fig. 1D). A control reaction was performed with wild-type human PiT-2 (wild type). Signals corresponding to glycosylated (gly+) and deglycosylated (gly-) species are indicated. The deduced orientation of C-terminal-truncation mutants in vesicles is indicated. Molecular mass markers are in kilodaltons.