TABLE 2.
Characteristics of the best-fitting modelsa
| Model | Comparison group | Interaction term? | SHIV variant
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHIV-KB9(−225)
|
SHIV-KB9(−305)
|
|||||
| F (df) | R2 (%) | F (df) | R2 (%) | |||
| Nonlinear exponential decayb | SHIV-KB9/SHIV-KB9ecto | No | 51 (4, 37) | 83 | 65 (4, 37) | 86 |
| Yes | 50 (5, 36) | 86 | 66 (5, 36) | 89 | ||
| Inversec | SHIV-KB9/SHIV-KB9ecto | No | 16 (3, 37) | 54 | 15 (3, 37) | 51 |
| Yes | 23 (4, 36) | 69 | 35 (4, 36) | 77 | ||
The relationship between cumulative antigenemia and the CD4+ T-lymphocyte set point in the SHIV-infected monkeys was analyzed using a nonlinear exponential decay model or an inverse model (23, 67). Each model was considered with or without a virus group-replication interaction term; the interaction term allowed the shapes of the curves to vary independently by virus group. The F statistic describes goodness of fit, and the adjusted R2 value describes the proportion of variability explained by the model (23, 33). The degrees of freedom (df) for the F statistics are shown in parentheses. The F statistics and adjusted R2 values for the comparisons of the SHIV-KB9(−225) and SHIV-KB9(−305) viruses with the SHIV-KB9/SHIV-KB9ecto group are shown for each model.
The formula for the nonlinear exponential decay model with interaction term is 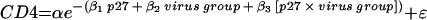 , where CD4 is the CD4+ T-lymphocyte set point and p27 is the cumulative p27 antigenemia.
, where CD4 is the CD4+ T-lymphocyte set point and p27 is the cumulative p27 antigenemia.
The formula for the inverse model with interaction term is CD4 = 1/(β0 + β1 p27 + β2 virus group + β3 [p27 × virus group]) + ɛ, where CD4 is the CD4+ T-lymphocyte set point and p27 is the cumulative p27 antigenemia.
