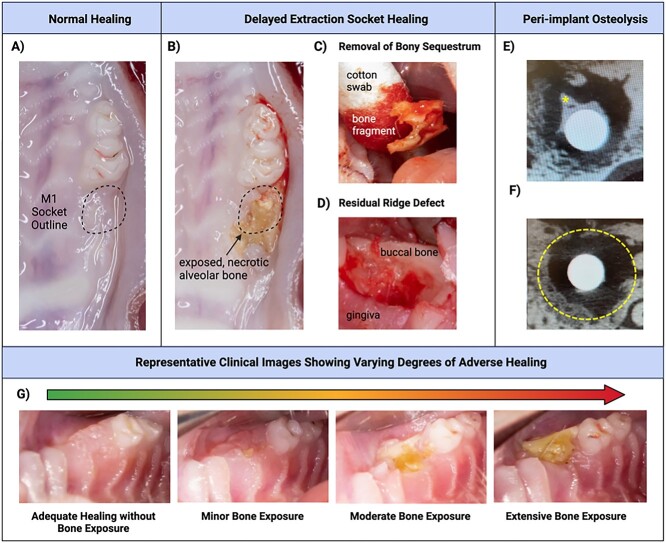
Figure 2.
Clinical findings. (A) Example of normal alveolar bone ridge healing without residual root tips, ridge defect, or bone exposure apparent clinically. (B) Adverse healing outcome involving necrotic, exposed bone. (C) Removal of exfoliated bone sequestrum. (D) Example of ridge defect with significant concavity in extraction site precluding implant placement. (E-F) Representative images of partial peri-implant healing with some bone formation on the implant surface (asterisk) amidst poorly defined lucent, mixed, or sclerotic lesion, sequestrum, periosteal proliferation and/or destruction of adjacent structures (radiological signs of an osteonecrosis). Dashed line shows peri-implant osseous well-defect border. (G) Representative clinical intraoral images showing varying degrees of osteonecrosis, from no visible bone exposure to mild, moderate, and extensive bone exposure.