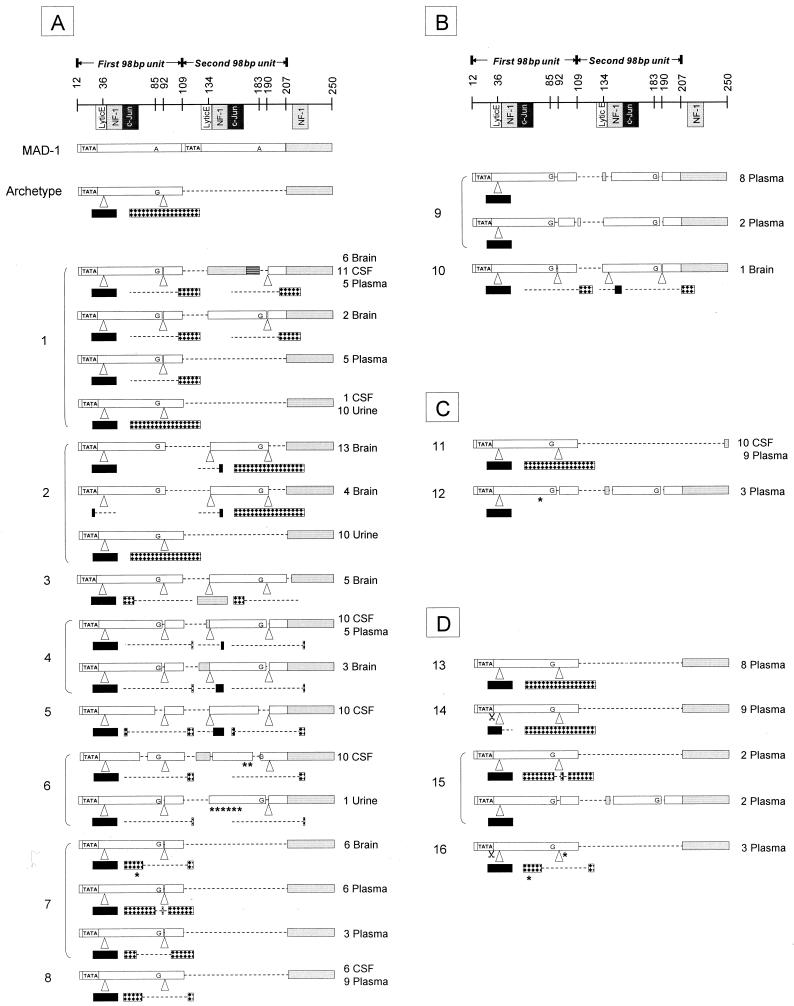
FIG. 1.
Sequencing results of the JCV RR. On the top is a representation of the MAD-1 and archetype JCV RR. The nucleotide numbers are based on the prototype MAD-1 sequence. The known transcription regulation factor binding sites are indicated and include the lytic control element (Lytic E), nuclear factor 1 (NF-1), and c-Jun. Each 98-bp unit is represented by an open box. The TATA box is represented by TATA. The archetype contains only one 98-bp unit with two inserts. Black box, 23-bp insert; checkered box, 66 bp-insert; dotted lines, deletions in the 98-bp units or in the 23- or 66-bp inserts; grey box, region downstream of the 98-bp units. Some clones contain fragments of this region inserted in the second 98-bp unit. MAD-1 contains an adenine at positions 85 and 183, compared with all other sequences that contain guanine at these positions. Asterisks, single mutations; scissors, single nucleotide deletions in the TATA box. (A) Sequencing results of HIV+ PML progressor patients 1 to 8. At the right of each sequence is the number of clones obtained per anatomic compartment. The first sequence of patient no. 1 has a large deletion in the second 98-bp unit that is replaced by a fragment identical to nucleotides 208 to 247 (striped box) containing an NF-1 predicted binding site and next to it a c-Jun binding site. Patient 3, 4, and 6 sequences have smaller fragments of the region nt 208 to 250 inserted in the second 98-bp unit; only the patient 3 sequence contains the full length of the NF-1 binding site. (B) HIV-negative PML progressors. (C) PML survivors. No. 11 is HIV+ and no. 12 is HIV−. (D) HIV+ patients with low CD4+ T-cell counts and other, non-PML neurologic disorders.