Fig. 5. ASC-CCM ameliorates increased oxidative stress in rOBI mice and decreased catalase activity in oxidatively stressed Müller cells in vitro.
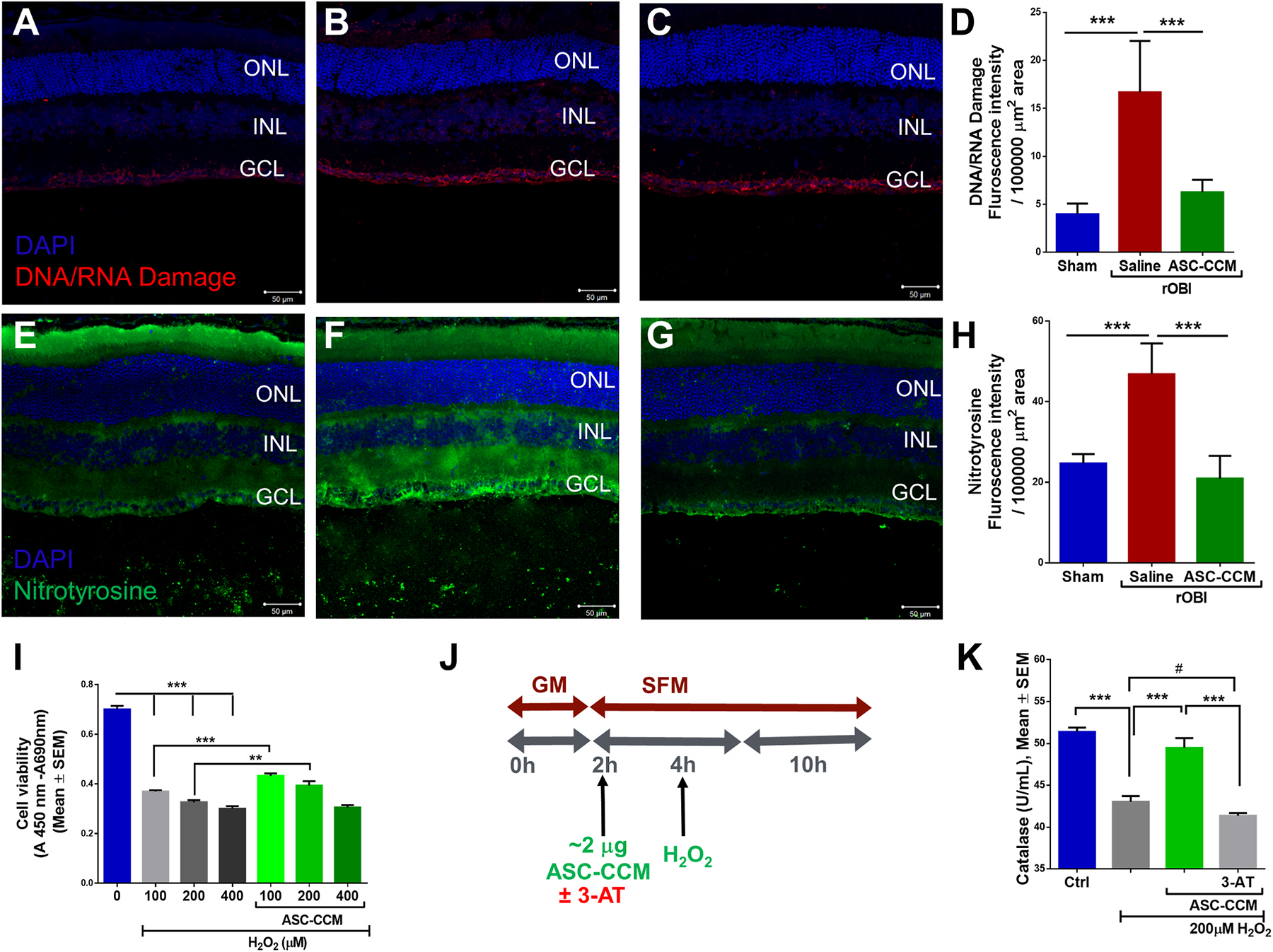
Immunohistological analysis of retinal tissue for DNA/RNA damage marker antibody followed by confocal microscopy in (A): Sham mice recieveing saline (B): rOBI mice receiving saline, (C): rOBI mice receiving ASC-CCM, and (D): Image J quantification of DNA/RNA damage marker intensity for all groups. Immunohistological analysis of retinal tissue for anti-nitrotyrosine antibody followed by confocal microscopy in (E): Sham mice receiving saline (F): rOBI mice receiving saline, (G): rOBI mice receiving ASC-CCM, and (H): Image J quantification of anti-nitrotyrosine immunostaining intensity for all groups. Data in (D&H) represent Mean ± SEM from n = 4–6 animals/group. ***, p < 0.001. (I): Cell proliferation/viability was assessed with WST-1 Cell Proliferation Assay System in rMC-1 cells. (J): Schematic representation of pretreatment of ASC-CCM with 3-AT (0.5 mM of 3-Amino-1,2,4-triazole) and H2O2 exposure in rMC-1 for catalase activity assay. (K): Biochemical measurement of catalase activity in cell lysates from rMC-1 cells. Data represent Mean ± SEM from replicate measurements repeated independently. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; #, p > 0.05.
