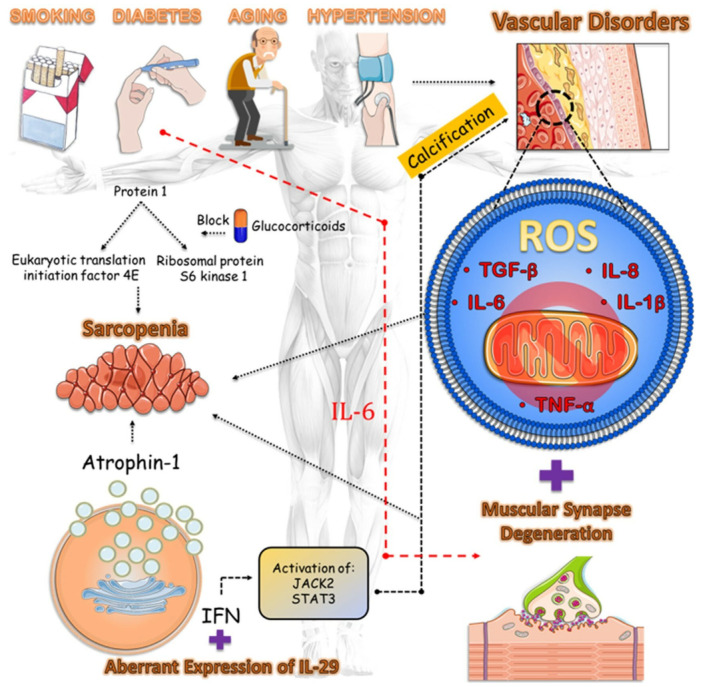
Figure 2.
Vascular problems and neurodegeneration resulting in sarcopenia: Vascular disorders can lead to reduced nutrition and minimal oxygen supply to cells. In this context, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are formed due to energy problems in the cell, forming pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 (interleukin-6), IL-8, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β). In addition, excess interleukin-29 (IL-29) exocytosis worsens vascular problems by activating Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) and signal transducer and activation of transcription signal 3 (STAT3). This scenario, associated with impaired muscle synapses, may result in sarcopenia, impacts on quality of life and usual activities, and increasing mortality.