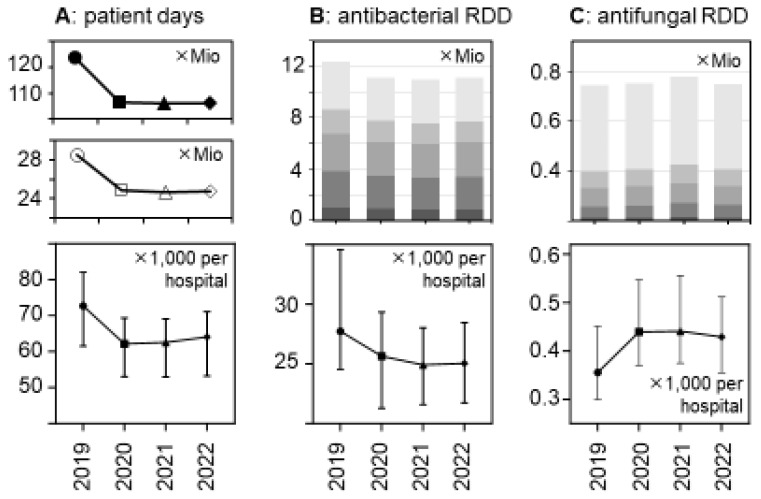
Figure 1.
Changes between 2019 and 2022 in patient days and antibacterial and antifungal drug use volumes (in RDDs) in German acute care hospitals. (A) The upper panel shows the number of patient days in all German general hospitals; the middle panel shows the number of patient days in the acute care hospital sample (n = 279) of the present study, and the lower panel shows the median patient days per participant hospital (±95%CI). (B) The upper panel depicts the total number of antibacterial drugs (in RDDs) dispensed in the participant hospitals, stratified by hospital size/type ( , very small;
, very small;  , small;
, small;  , medium-sized;
, medium-sized;  , large; and
, large; and  , university hospitals); the lower panel shows the median antibacterial RDDs per participant hospital (±95%CI). (C) Similar to B for antifungal drugs (n = 272 hospitals). The changes over time were statistically significant in a hospital-level analysis (lower panels) according to a Friedman one-way repeated measure analysis of variance by rank and after Dunn’s post hoc multiple comparisons (of each year versus 2019).
, university hospitals); the lower panel shows the median antibacterial RDDs per participant hospital (±95%CI). (C) Similar to B for antifungal drugs (n = 272 hospitals). The changes over time were statistically significant in a hospital-level analysis (lower panels) according to a Friedman one-way repeated measure analysis of variance by rank and after Dunn’s post hoc multiple comparisons (of each year versus 2019).