Figure 1.
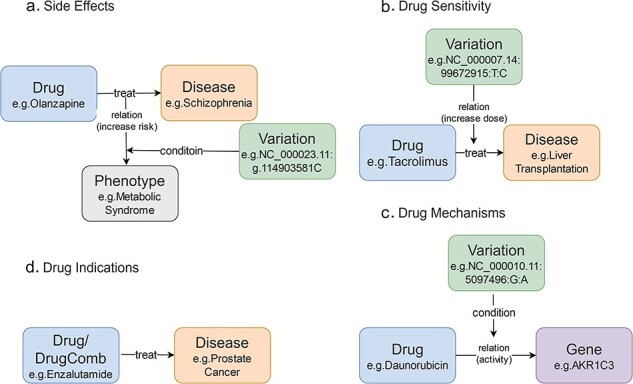
Knowledge patterns in CPMKG. (a) Side effects refer to side effects or complications that occur during the use of medication. Example: association between olanzapine and metabolic syndrome risk in schizophrenia patients. (b) Drug sensitivity refers to an individual’s propensity to exhibit a heightened or exaggerated response to medication compared to the average population. Example: influence of the CC genotype on tacrolimus requirement in liver transplant patients. (c) Drug mechanism refers to the relationship between an individual’s genome and their response to medications. Example: reduction of AKR1C3 enzyme activity during daunorubicin treatment in patients with the A allele variant. (d) Drug indication refers to the formal recommendation for medication use in treating specific diseases or pathological conditions. Example: utilization of enzalutamide in prostate cancer treatment.
