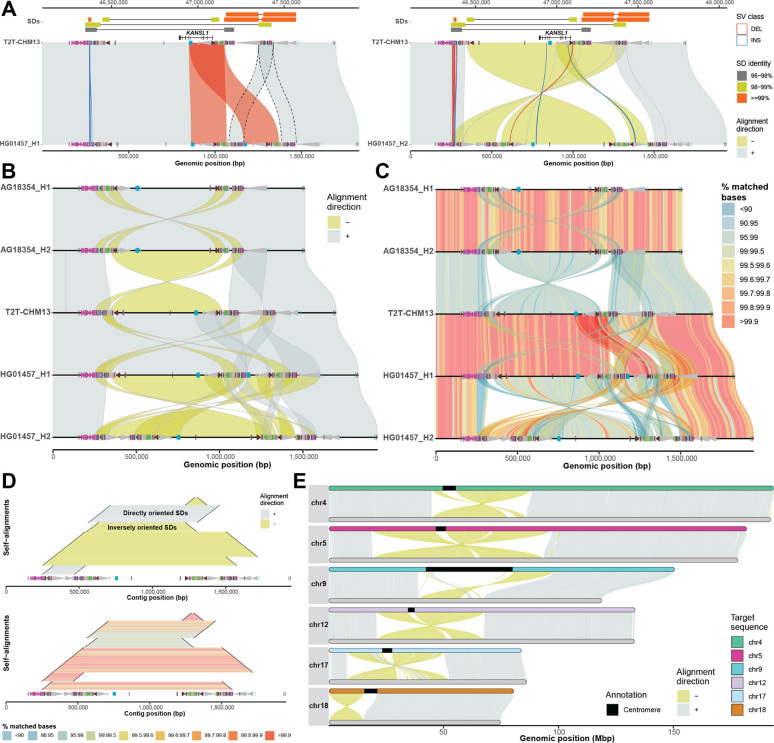
Figure 1: Example of SVbyEye visualization modes.
A) The plot depicts a minimap alignment of a 1.7 Mbp region from chromosome 17q21.31 of two human sequences: HG01457 haplotypes (query) vs. T2T-CHM13 reference (target). Segmental duplication (SD) pairwise alignments are shown (top) (connected by horizontal line) colored by their sequence identity with gene annotation (KANSL1 exons) depicted below as annotated in the UCSC Genome Browser. Minimap2 alignments are shown as gray (forward ‘+’ orientation) and yellow (reverse ‘−’ orientation) polygons between query (bottom) and target (top) sequences. Duplicon annotations as defined by DupMasker (Jiang et al. 2008) are indicated for both query and target sequences by colored arrowheads pointing forward or backward based on their orientation. An SV embedded within the SDs between query and target sequences (≥1 kbp) is highlighted as blue (insertion) and red (deletion) outlines facilitating breakpoint definition. B) A “stacked” SVbyEye plot depicting the 17q21.31 region for two chimpanzee haplotypes followed by three human haplotypes from T2T-CHM13 and HG01457. Each sequence is compared to the sequence immediately above and clearly defines a 750 kbp inversion between chimpanzee and human flanked by inverted repeats. A larger 900 kbp inversion polymorphism is also identified in human mediated by inverted SDs. C) The plot shows the same alignments as in B but with a “% identity grid” colored by the percentage of matched bases per 10-kbp-long sequence bin. Human inversion shows significant divergence indicating a deeper coalescence of the 17q21.31 region (Zody et al. 2008). D) A ‘horizontal dotplot’ visualization that shows self-alignments of HG01457 (haplotype 2) indicating the size (black line), the orientation (inverted=yellow and gray=direct; top panel), and the pairwise identity (colored grid; bottom panel). The largest and most identical segments are preferred sites for non-allelic homologous recombination (NAHR) breakpoints. E) A T2T view of six chimpanzee chromosomes (query, bottom) aligned to human syntenic chromosomes (T2T-CHM13, target, top). This view readily defines the extent of paracentric and pericentric inversions.