Fig. 3. PM cholesterol accessibility increases during EC activation and influences the magnitude of VCAM-1 induction.
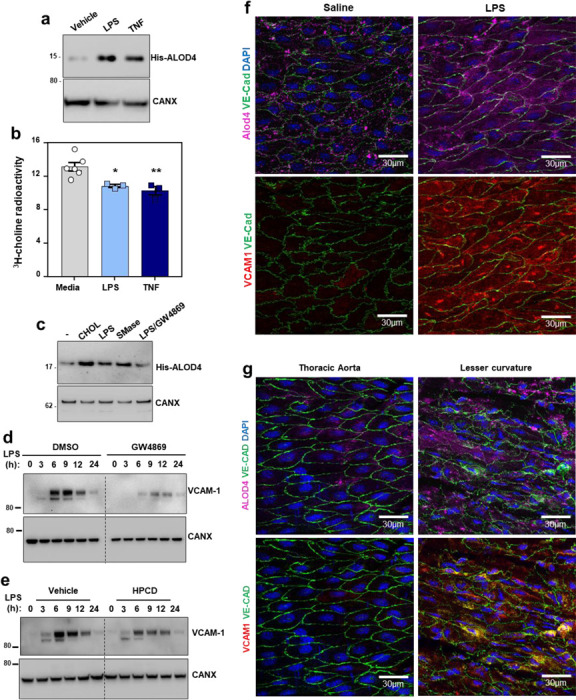
(a) Western blot to assess His-ALOD4 binding to the surface of HUVECs exposed to either LPS (100 ng/ml) or TNFα (10 ng/ml) for 1 h. (b) [3H]-choline-labeled SM in HAECs after incubation with LPS (100 ng/ml) or TNFα (7.5 ng/ml) for 40 mins. (c) Western blot to assess His-ALOD4 binding to the surface of HAECs treated with MβCD-cholesterol (100 μM), LPS (100 ng/ml), bacterial nSMase (1 U/ml), or LPS co-incubated with the neutral sphingomyelinase inhibitor GW4869 (5 μM) for 1 h. (d) Western blot for VCAM-1 in HUVECs pre-treated with or without GW4869 (10 μM) for 30 mins before exposure to LPS for the indicated times. (e) VCAM-1 in HUVECs treated with LPS for 30 mins before being incubated with or without HPCD for 15 mins. After washing away the HPCD, cells were incubated with media containing 10% FBS for the indicated times. (f) ALOD4–647 binding to the thoracic aorta of female mice after i.p injections of either saline or LPS (60 μg per mouse) for 3 h. Samples were co-stained with VCAM-1 (red), Ve-cadherin (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 30 μm (g) ALOD4–647 binding to thoracic aorta or the aortic arch (lesser curvature) of female mice. Samples were co-stained with VCAM-1 (red), Ve-cadherin (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 30 μm. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
