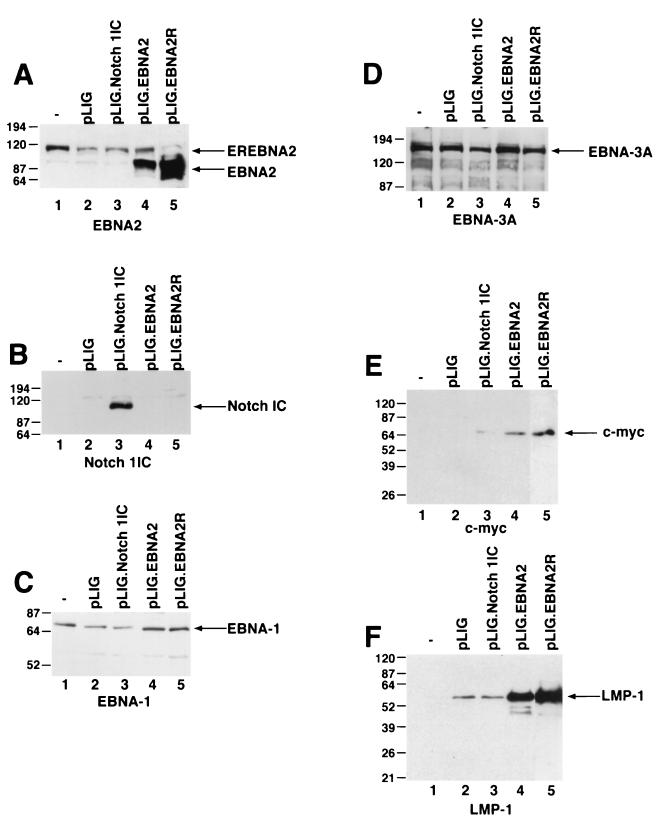
FIG. 6.
Detection of EBNAs, LMP-1, and c-myc in EBNA2- and Notch1IC-expressing EREB2.5 cells after estrogen withdrawal. (A) Western blot of cellular extracts derived from cells starved for estrogen for 4 days. The blots were probed with the PE2 monoclonal antibody directed against EBNA2. Both the EREBNA2 and wild-type EBNA2 genes can be detected and are indicated by arrows. The cell lines used are indicated above the blot. −, parental EREB2.5 cells were used as a control. pLIG.EBNA2R is a cell line expressing wild-type EBNA2 from pLIG and grown long-term in media lacking estrogen. (B) Same as for panel A, except that the blot was probed with an anti-Notch1 antisera. (C) Same as for panel A, except that the blot was probed with an anti-EBNA-1 antibody. (D) Same as for panel A, except that the blot was probed with an anti-EBNA-3A antibody. (E) Same as for panel A, except that the blot was probed with an anti-c-myc antibody. (F) Same as for panel A, except that the blot was probed with an anti-LMP-1 antibody. Migration of molecular weight markers is shown to the left of each blot, and the specific proteins detected are indicated by the arrows on the right.