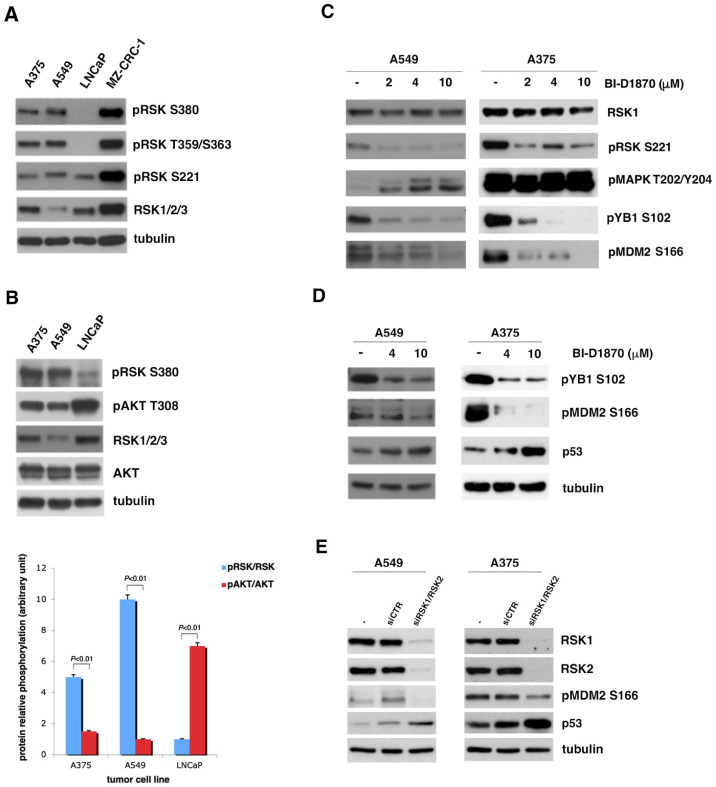
Figure 1.
p90RSK induces p53 degradation by phosphorylating MDM2 at S166. (A) Several human tumor cell lines (A375, A549, LNCaP, MZ-CRC-1) were analyzed for the phosphorylation of p90RSK at different sites (pRSK S380, T359/S363, S221) and for the total level of p90RSK (RSK1/2/3). Tubulin was used to normalize. (B) The A375 the A549 cell lines, melanoma and lung cancer, respectively, were compared to the LNCaP prostate cancer cell line for the phosphorylation levels of p90RSK at S380 (pRSK S380) relative to total proteins (RSK1/2/3) and for the phosphorylation levels of AKT on T308 relative to total proteins (AKT). Tubulin was used for normalization (upper panel). The bar diagram below shows the ratio between the phosphorylated form and the total protein (pRSK/RSK and pAKT/AKT) obtained by quantifying each sample with the ImageJ program. Standard deviations were derived from three different quantifications (bottom panel). (C) A549 and A375 were incubated with the indicated doses of BI-D1870 for 1 h. The BI-D1870 inhibition efficacy was confirmed by the anti-phospho-S102 YB1 and anti-phospho-S221 RSK antibodies. Phosphorylated ERK1/2 antibody (pMAPK T202/Y204) was used to check the specificity of the inhibition. Phosphorylated MDM2 was visualized with anti-phospho-S166 MDM2 (pMDM2 S166) antibody. Anti-RSK1 antibody (RSK1) was used to normalize the immunoblot. (D) A549 and A375 cells were incubated with the indicated concentration of BI-D1870 inhibitor. The BI-D1870 effect was monitored by using the anti-phospho-S102 YB1 (pYB1 S102) antibody. Phosphorylated MDM2 was highlighted with anti-phospho-S166 MDM2 (pMDM2 S166) antibody. The p53 protein amount was determined using anti-p53 (p53) antibody. Anti-tubulin antibody was used to normalize the immunoblot. (E) A549 and A375 cells were transfected with a pool of specific RSK1/RSK2 siRNAs for interference against RSK1 and RSK2 or with control siCTR. To evaluate the efficiency of interference, we used anti-RSK1 and anti-RSK2 antibodies. The level of MDM2 phosphorylation was visualized with anti-phospho-S166 MDM2 antibody. The p53 level was determined by the use of anti-p53 antibody. Anti-MDM antibody was used for normalization. All experiments presented were repeated three times with consistent results. Furthermore, to also measure the relative contribution of AKT to MDM2 phosphorylation at S166, as described in literature [33], we analyzed the T308 phosphorylation of AKT in the A549 and A375 cells compared to that in the LNCaP cells (Figure 1B). It is immediately evident that in cells in which p90RSK is highly activated (A549 and A375 cell lines), AKT appears less phosphorylated than in the LNCaP cell line, which presents very active AKT, as expected due to PTEN mutation, but does not present strong phosphorylation of p90RSK.