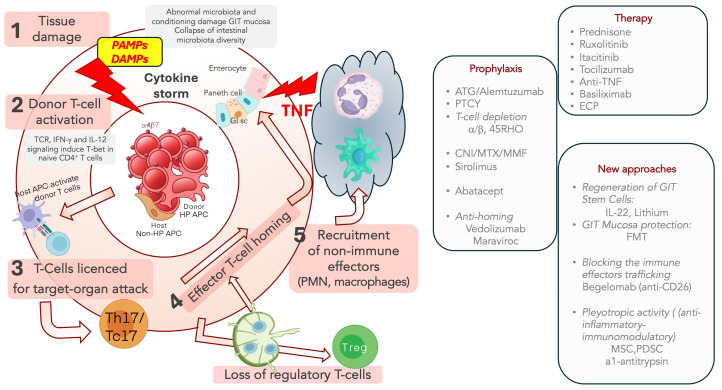
Figure 1.
Pathogenesis of aGVHD and main targetable pathways for prophylaxis and treatment. Simplified outline of the aGVHD pathogenesis and the possible specific interventions according to some targetable steps. 1—The conditioning damages host tissues and causes the release of inflammatory mediators with the activation of host APCs; this process is amplified in the GIT lumen, where the altered microbiota and the destruction of the intestinal barrier facilitate the stimulation of innate immunity. 2—Host APCs activate donor T cells in the secondary satellite lymphoid organs 3—After expansion in the lymph nodes, activated T cells are primed, differentiating to type 1 T helper (Th1)/type 1 CD8+ T (Tc1) or Th17/Tc17 cells, and become able to target specific organs; 4—The lymphocyte traffic to the target organs is mediated by adhesion molecules such as L-selectin, CCR7, integrin a4b7; 5—activated T-cells can induce the tissue damage, both directly and by recruiting non-immune effector cells, (such as monocytes, PMN and NK) cells, and cytokines, such as TNF. The progressive loss of Treg contributes to the uncontrolled expansion of alloreactive T cells. Targetable pathways for Prophylaxis: 1—alloreactive T-cell depletion (in vivo/ex vivo): ATG; Campath; 2—early PTCy blocks alloreactive donor T cell expansion; 3—CD34 + selection/a-b depletion; 4—inactivating TCR (CNI: CSA, Tac); Sirolimus is a mTOR inhibitor which inhibits effector T-lymphocytes; 5—Abatacept (CTLA4-Ig) blocks T cell-APC co-stimulation; 6—Anti-homing compounds interfere with the alloreactive T-cell migration in the target organs (Vedolizumab; Maraviroc). Targetable pathways for Therapy: 1—anti-inflammasome treatment (Prednisone; Ruxolitinib/Itacitinib; Tocilizumab; Etanercept/Infliximab; 2—blocking T-cell priming: anti-IL2 (Basiliximab); 3—Primed T cells are susceptible to the Jak1/2 inhibitor Ruxolitinib or anti-IL-6R-antibodies (Tocilizumab) anti-TNF-antibodies; 4—Begelomab (anti-CD26) blocks alloreactive T cell migration to target organs; 5—treatments aimed to protect or regenerate target organs: IL22, FMT, anti-1 anti-trypsin; 6—Agents with pleiotropic activity: MSC; PDSC; multitarget treatments (ECP induces tolerogenic dendritic cells; reduces inflammasome; augments Treg). Abbreviations: aGVHD, acute GVHD; GIT, gastrointestinal tract; GIsc, gastrointestinal stem cells; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; HP APC, hematopoietic antigen-presenting cell; non-HP APC, non-hematopoietic antigen-presenting cell; TCR, T cell receptor; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; Th, helper T lymphocyte; Tc, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; T reg; regulatory T cells; PMN, polymorphonucleated cells; NK, natural killer cells; PTCY, post-transplant cyclophosphamide; CNI, Calcineurin Inhibitor; CSA, cyclosporine A; Tac, Tacrolimus; MTX, Methotrexate; MMF, Mycophenolate; ECP, Extracorporeal Photopheresis; FMT, fecal microbial transplant; MSC, mensenchimal stem cell; PDSC, placenta-derived stem cells.