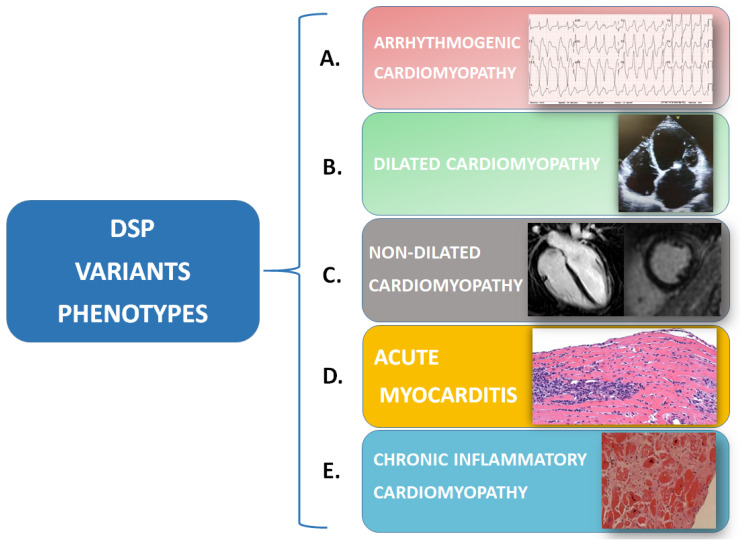
Figure 3.
Desmoplakin variants can cause a spectrum of phenotypes, which can sometimes coexist at the same moment or can be expressed in the same patient at different times: (A) Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy is characterized by EKG anomalies and a high arrhythmic burden (i.e., right bundle-branch block morphology ventricular tachycardia) that can be associated with morphological/functional anomalies of one or both ventricles. (B) Dilated cardiomyopathy is characterized by isolated or biventricular dilatation and global or regional systolic dysfunction. (C) Non-dilated cardiomyopathy is defined by the presence of morphological anomalies (i.e., ring-like LGE at CMR) or isolated systolic dysfunction of one or both ventricles. (D) In acute myocarditis, endomyocardial biopsy shows a white blood cell infiltration of the myocardium that can be associated with anomalies of cardiomyocytes, apoptosis, and/or signs of necrosis. (E) In chronic inflammatory cardiomyopathy endomyocardial biopsy samples, fibrosis predominates over white blood cell infiltration.