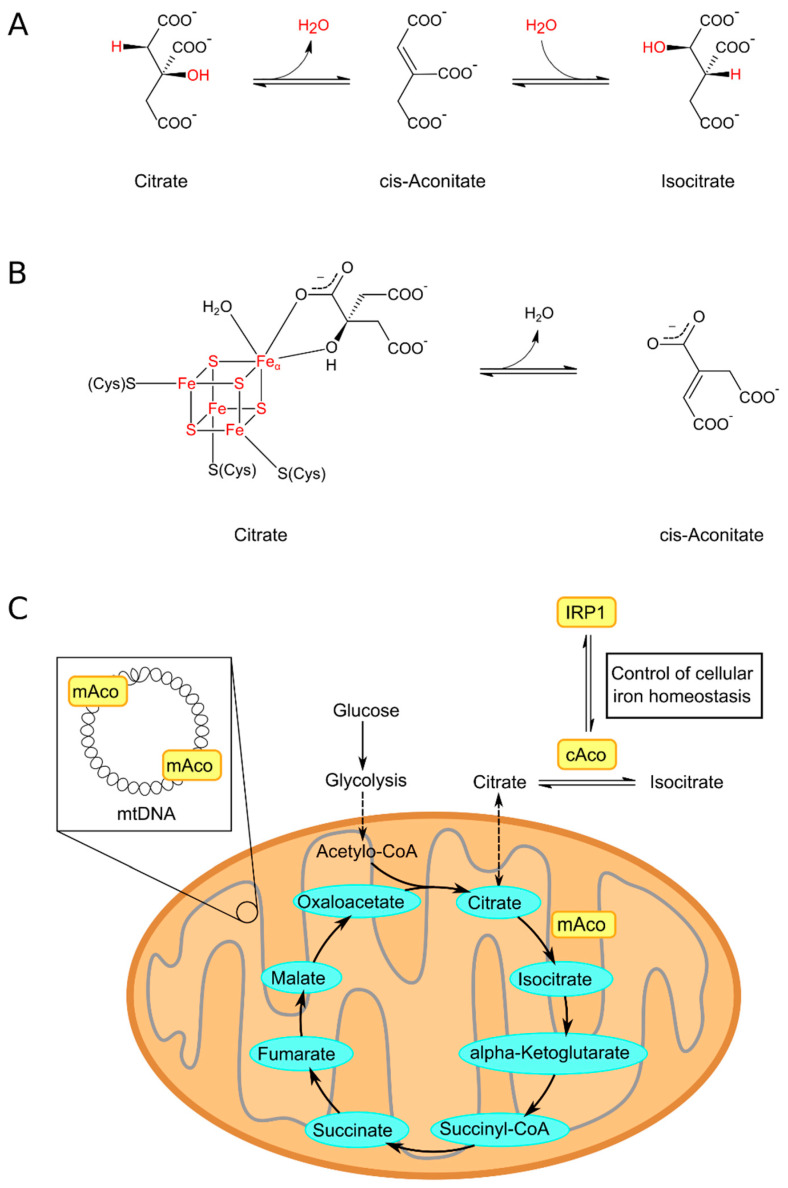
Figure 1.
Aconitase engagement in the TCA cycle. (A) Aconitase isomerization citrate to isocitrate; (B) The mechanism of aconitase reaction. The transformation of citrate to cis-aconitate is promoted by the ISC. The supplement of labile Feα converts an inactive aconitase into its active form and coordinates with oxygen atoms of citrate and water molecules to promote the reaction catalysis; (C) Aconitase cellular localization. cAco—cytosolic aconitase (Aco1); mAco—mitochondrial aconitase (Aco2). The redox state of the Aco1 ISC defines the function of the enzyme. IRP-1 is an oxidized (apo-) form of cAco, which takes part in maintaining iron homeostasis in the cell, whereas the reduced (holo-) form—similar to Aco2—accomplishes the isomerization of citrate into isocitrate. Additionally, Aco2 is a protein with a role in the stabilization of mtDNA.