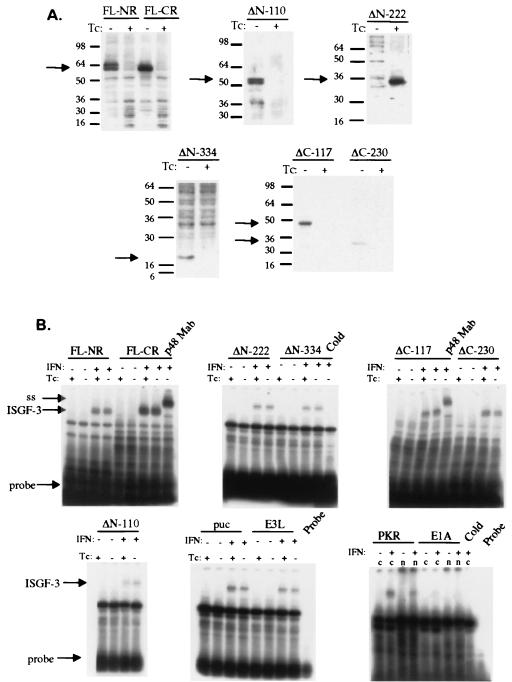
FIG. 1.
Effect of NS5A expression on IFN signal transduction. (A) Tetracycline (Tc)-regulated expression of full-length and mutant NS5A proteins. FL-NR denotes a full-length NS5A construct derived from an IFN-nonresponsive patient, while FL-CR denotes a full-length NS5A construct derived from an IFN-responsive patient. ΔN-110, ΔN-222, ΔN-334, ΔC-117, and ΔC-230 represent NS5A deletion mutants lacking 110, 222, 334, amino acids from the amino terminus and 117 and 230 amino acids from the carboxy terminus, respectively. Protein positions are shown by arrows. Western blots were probed with HCV-infected patient serum as described in Materials and Methods. (B) Effect of NS5A expression on ISGF-3 induction. Plasmids were transiently transfected into HeLa Tet-Off cells, grown in the absence and presence of tetracycline to induce and repress NS5A, respectively, and treated with IFN to induce ISGF-3. Protein extracts were hybridized to a 32P-labeled oligonucleotide corresponding to the consensus ISRE. “puc” represents a control transfection with the pTRE-puc parental plasmid with no insert. “E3L,” “PKR,” and “E1A” represent expression of the E3L, PKR, and E1A proteins, respectively. The p48 monoclonal antibody used to form supershifts (denoted by “ss” and an arrow) is denoted by “p48 Mab”. “n” and “c” represent nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts, respectively. ISGF-3 is induced only with IFN treatment and is indicated with arrows.